
Choosing between LlamaIndex and LangChain is less about picking the “better” framework and more about understanding which one matches how you’re building. Both help you move from raw language models to production AI systems, but they sit at different layers of the stack and excel in different places.
This LlamaIndex vs LangChain guide takes a practical approach. We’ll cover architecture, retrieval patterns, performance trade-offs, tooling, and how each framework works with self-hosting n8n on a VPS. By the end, you’ll know whether your project needs orchestration-first tools, data-first infrastructure, or both running side by side.
Developers evaluating LlamaIndex vs LangChain usually arrive from two directions. Either they need help orchestrating prompts, tools, and multi-step reasoning, or they need a reliable way to connect an LLM to private documents and databases. LangChain leans toward orchestration and agents. LlamaIndex (formerly GPT Index) is a data framework built to make retrieval-augmented generation simpler to ship and operate.
In 2026, teams rarely deploy raw models. They use frameworks to manage LangChain chains, memory, retrieval pipelines, and evaluation. Understanding how LlamaIndex and LangChain think about context, agents, and tools helps you decide whether to start with one, the other, or combine them from day one.
Most real projects don’t force an either-or decision. Many production stacks use LlamaIndex as the knowledge layer, LangChain as the orchestration layer, and n8n as the workflow engine tying them together on a VPS or Dedicated Server.
What Is LangChain?
LangChain is a framework for building LLM-powered applications that connect language models with tools, data sources, and multi-step workflows. It’s a toolkit that breaks complex AI behavior into composable building blocks instead of cramming everything into one massive prompt.
Those building blocks are the LangChain components. Common ones include models, prompt templates, memory, retrievers, and output parsers. You combine them into LangChain chains, where each step uses an LLM or tool to move the task forward. A chain might retrieve documents, summarize them, generate a response, then log the result. Each piece connects to the next, just like the links of a chain.
On top of chains sit LangChain agents. These introduce decision-making. Given a goal and a set of tools, an agent chooses which tool to call next, observes the output, and repeats until the task is done. Agents work well when tasks involve branching logic, external APIs, and multi-step reasoning that you can’t predict in advance.
LangChain prompts and templates define how you structure requests to the model. Instead of hardcoding prompts, you create templates with variables that get filled at runtime. This makes prompts reusable and easier to version. LangChain models are pluggable: OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, or local LLMs all slot into the same abstraction, letting you adjust cost and performance without rewriting your pipeline.
Installing LangChain fits normal Python or node.js workflows. You add it via Python or node.js managers, configure model providers using environment variables or config files, then wire chains or agents into your services. From there, you expose them behind APIs that n8n or other workflow tools can call.
What Is LlamaIndex?
While LangChain focuses on orchestration, LlamaIndex focuses on data. It functions as a data framework for connecting your documents, databases, and APIs to LLMs using flexible indices and query engines. It powers retrieval-augmented generation by turning your content into structured knowledge the model can reliably query.
The main LlamaIndex components are data connectors, node parsers, indices, and query engines. You ingest data from sources like S3, Postgres, file systems, or APIs, chunk them into nodes, then build indices. Options include vector indices, list indices, tree indices, keyword indices, and graph indices. Each one trades off speed, accuracy, and complexity differently.
At query time, LlamaIndex routes queries through these indices and synthesizes responses. The framework handles chunk selection, ranking, and context assembly so you get relevant passages inside the model’s context window without manually building that pipeline every time.
Recent versions also add LlamaIndex agents, which execute multi-step plans over your indices and tools. But the framework still keeps data access and retrieval as the main storyline. If your biggest problem is “I have a lot of documents and need accurate answers,” LlamaIndex is usually the place to start.
LangChain context and LangChain models can integrate with LlamaIndex retrievers, and many teams run both frameworks side by side. LangChain handles orchestration and tool routing; LlamaIndex handles data ingestion, indexing, and retrieval. This division of labor works well when you need both flexibility and reliability.
LlamaIndex also offers different index types for different use cases. Vector indices work well for semantic search. Tree indices optimize for hierarchical documents. Keyword indices handle exact match scenarios. You pick the index type based on your data structure and query patterns, then let the framework optimize retrieval and response synthesis.
LangChain vs LlamaIndex: Core Architectural Differences
Comparing LangChain vs LlamaIndex means looking at how each structures an AI application. LangChain builds around prompts, tools, and agents. LlamaIndex builds around data connectors, indices, and query engines. Both can power similar end results, but the path you take through each framework is different.
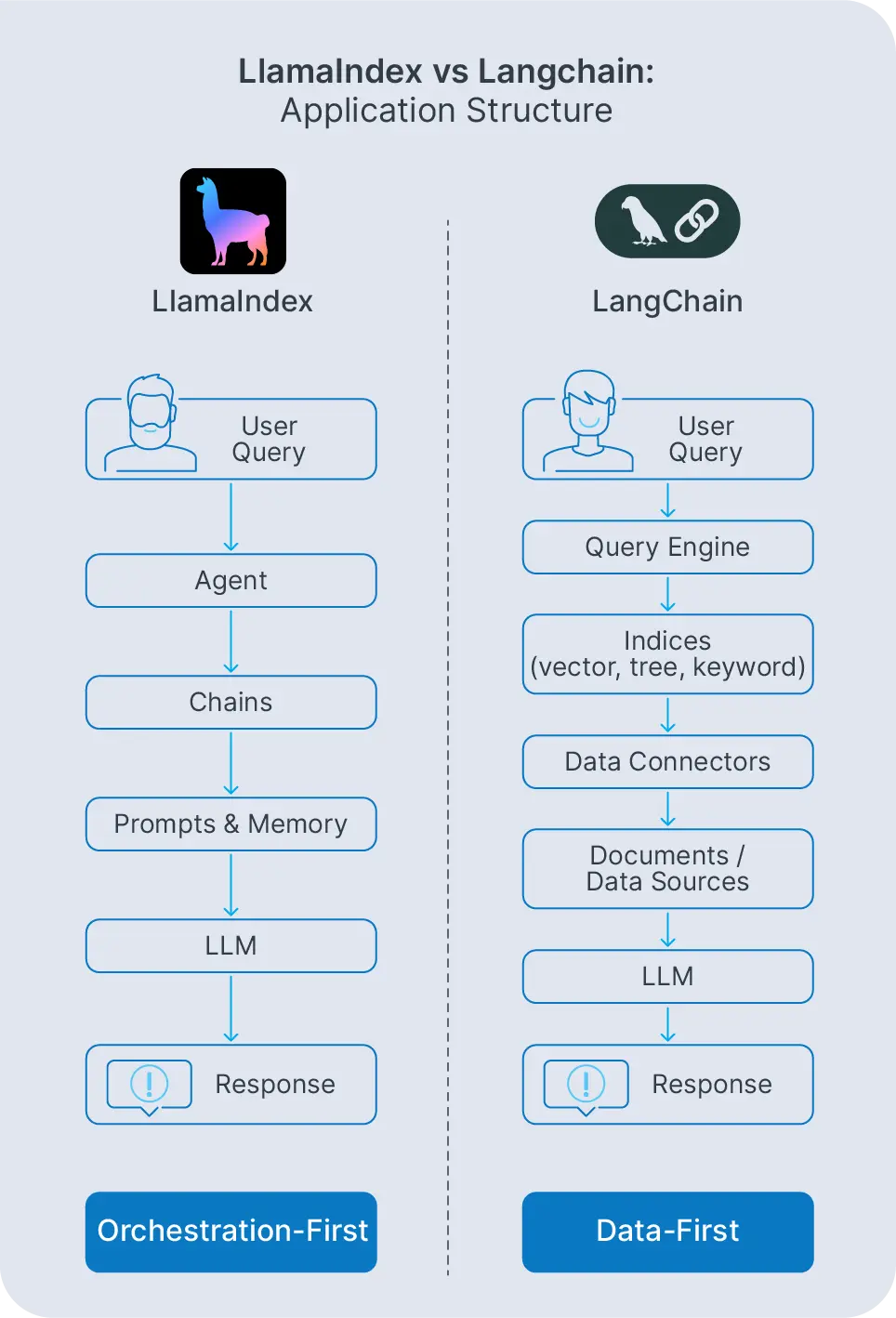
With LangChain, LangChain prompts and templates define how you talk to the model. Those prompts are wired into LangChain chains that orchestrate calls to models, tools, and retrievers, often with memory components storing conversation history or user-specific context. Chains run sequentially or conditionally depending on how you configure them.
LangChain models are pluggable. You swap OpenAI for Anthropic or Google without rewriting application logic. This abstraction matters when you’re optimizing costs or testing new models. You change one configuration line instead of refactoring your entire codebase.
LangChain agents sit on top of chains. These agents decide which tool to call next from a pool of options: web search, database queries, custom APIs, or file operations. They excel when tasks involve branching logic and external tools, such as research assistants, operations bots, or customer support copilots.
LlamaIndex takes a different route. LlamaIndex agents and query engines live on top of indices. Instead of orchestrating many tools, they orchestrate how your data is accessed: which index to query, how to combine results, how to generate final answers. The focus stays on retrieval and knowledge management rather than general orchestration.
LangChain can plug into LlamaIndex retrievers, and LlamaIndex can run inside LangChain agents. Many production systems use both. But when you zoom out, LangChain is primarily an orchestration engine, while LlamaIndex is primarily a data and retrieval engine. Teams that need both flexibility and grounded answers usually deploy them together instead of forcing an either-or decision.
LlamaIndex vs LangChain: Retrieval, Context, and Performance
Retrieval and context handling drive real-world LangChain performance and LlamaIndex performance more than any single model choice. Both frameworks can power RAG, but they structure that work differently and make different trade-offs.
In LangChain, you assemble LangChain retrieval using retriever abstractions plugged into vector stores such as Pinecone, Qdrant, or Postgres with pgvector. You decide how to chunk documents, embed them, store embeddings, and select results at query time. That flexibility is powerful but pushes more responsibility onto the developer for tuning LangChain context size, reranking strategies, and caching policies.
You control every step. This works well when you already have an opinionated storage layer or need custom logic around how documents are selected and ordered. But it also means you’re building and maintaining more infrastructure yourself.
LlamaIndex bakes these choices into its indices. You configure index types, chunking strategies, and query routing once, then rely on the framework to route queries efficiently. This has a direct impact on LlamaIndex performance, because the framework optimizes token usage, caching, and routing under the hood. It manages LlamaIndex context construction: which chunks to include, in what order, and with what metadata, to keep responses grounded while staying inside the context window.
LlamaIndex retrieval happens through query engines that know how to traverse tree indices, search vector indices, or combine results from multiple index types. The framework handles reranking, filtering, and synthesis steps that you’d otherwise build manually.
Practical performance comes down to caching, index choice, and chunking. With LangChain, you tune these manually. With LlamaIndex, you configure them once through index parameters and query settings. If you enjoy low-level control and already have a storage strategy, LangChain’s approach fits. If you’d rather treat retrieval as a high-level primitive and focus on schemas and sources, LlamaIndex usually gets you productive faster.
Lifecycle Management and Tooling in LangChain and LlamaIndex
Modern AI apps don’t stop at building a prototype. You need observability, versioning, rollback strategies, and safe deployments. This is where LangChain tools and surrounding infrastructure start to matter.
LangChain comes with a broad ecosystem: callbacks, tracing, and integrations with LangSmith for monitoring and evaluation. These LangChain tools let you inspect token usage, latency, and agent decisions, then improve chains based on real metrics. You can trace which tools an agent called, how long each step took, and where failures occurred.
Combined with logging from your hosting environment (n8n workflow logs, system metrics on a VPS), this forms a solid lifecycle story. You know when chains fail, why they fail, and how to fix them. You can run A/B tests on different prompt templates or model providers and measure which performs better in production.
On the LlamaIndex side, LlamaIndex tools focus on introspecting indices and query performance. You can explore how often specific documents are retrieved, tune index parameters, and run evaluation workloads over test queries. This is especially useful when your main risk is retrieval quality rather than chain logic.
LlamaIndex retrieval quality directly impacts whether your answers are accurate. The framework provides tools to measure retrieval precision, inspect which chunks were selected for a given query, and adjust index settings based on those results. You can also version indices, so rolling back to a previous data snapshot is straightforward.
Installation is similar for both frameworks. Installing LlamaIndex usually boils down to pip install llama-index plus configuration of model and embedding providers. Most teams wire both frameworks into the same environment, then use their observability tools plus standard DevOps practices (CI/CD, logging, alerts) on top.
LangChain with n8n for End-to-End AI Workflows
LangChain works best when you pair it with a workflow engine. n8n handles triggers, retries, and integrations; LangChain handles reasoning, prompts, and agents. This is where n8n LangChain integration becomes practical rather than theoretical.
Think of LangChain integration with n8n as giving your automations a “brain.” n8n pulls data from CRMs, ticketing systems, or internal APIs, then passes that context into LangChain chains or agents. Examples include summarizing long customer tickets before assignment, generating follow-up emails, or powering AI copilots for operations teams.
A typical flow looks like this: n8n triggers on a webhook or schedule, fetches data from external systems, sends it to a LangChain endpoint, receives a structured response, then routes that response to Slack, email, or a database. The division of labor is clean. n8n orchestrates the workflow. LangChain handles LLM reasoning and tool usage.
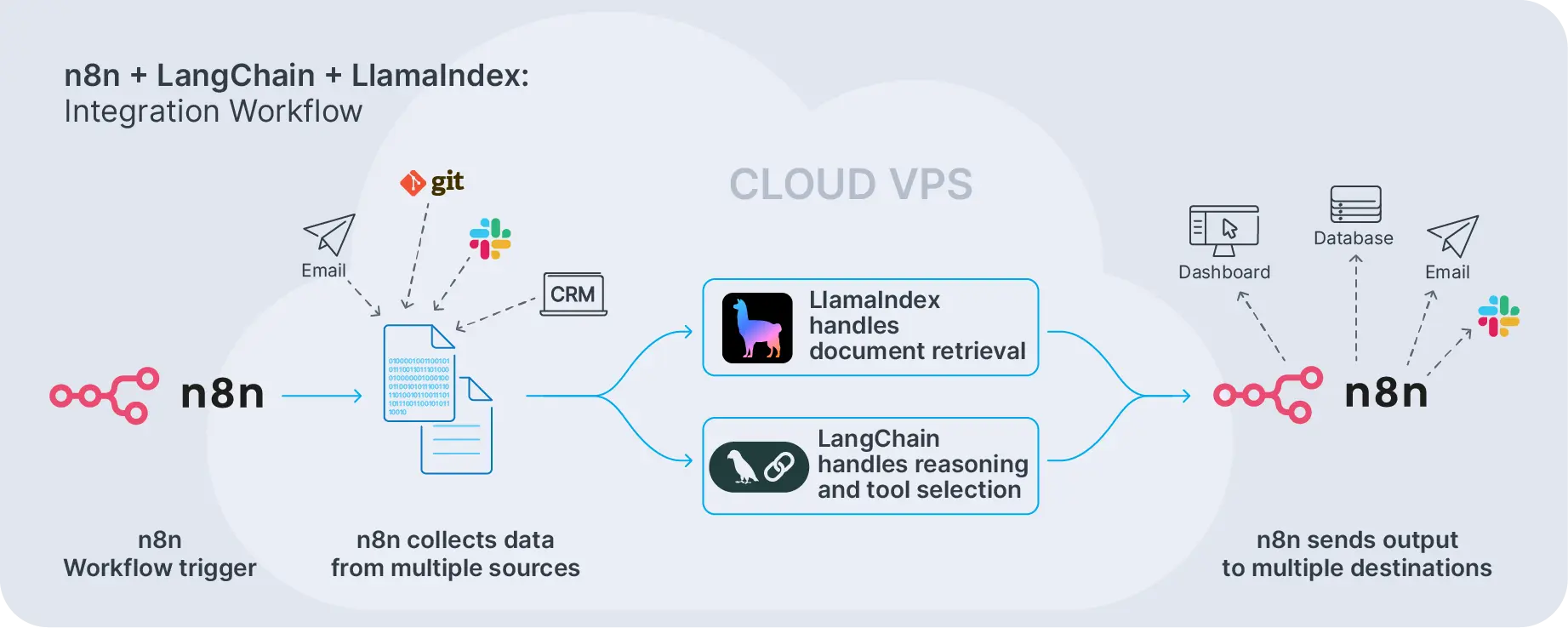
For deeper examples, you can explore patterns described in our article on n8n AI workflows and advanced integrations. In those setups, n8n orchestrates the whole process and calls LangChain where complex reasoning or LangChain prompts are needed.
This division works well on a Contabo VPS. n8n, LangChain code, and supporting services all run close together, minimizing latency and simplifying deployment. You don’t pay extra execution fees, and everything runs on infrastructure you control.
If you’re wondering how to use LangChain in n8n, the short version is: expose LangChain logic through a code node, an HTTP endpoint, or a containerized microservice, then call it from n8n nodes as part of your workflow. You can also embed LangChain retrieval directly in n8n code nodes if your workflows are simple enough.
LlamaIndex with n8n for Knowledge-Centric Automations
Where LangChain brings orchestration intelligence, LlamaIndex brings reliable knowledge. n8n LlamaIndex integration makes sense when your workflows depend on accurate answers over large document sets.
A typical pattern is: n8n ingests content from sources like S3, Git repositories, Notion, or internal wikis, then triggers index updates in LlamaIndex. The framework manages retrieval and LlamaIndex performance, while n8n handles scheduling, notifications, and downstream actions. For example, a weekly job might rebuild indices from updated policy documents, then let support agents query them through a chat interface.
This setup works particularly well when you need control over your data. If your documents include confidential contracts, internal roadmaps, or regulated information, running both n8n and LlamaIndex on infrastructure you control matters. You’re not handing documents to a third-party API or trusting that a cloud provider handles data residency correctly.
n8n LlamaIndex integration usually boils down to this: define HTTP endpoints or microservices around your LlamaIndex query engines, then use n8n’s HTTP Request node to call them from workflows. You can also trigger index updates from n8n whenever new files land in storage or a repository gets updated.
If you want to run this stack under your control, you can self-host n8n on a Contabo VPS and deploy LlamaIndex alongside it. This keeps your documents, embeddings, and queries on infrastructure you manage.
Workflows where precise retrieval matters include internal documentation Q&A, long-form report generation, customer knowledge bases, and compliance audit trails. In all of these cases, cperformance and retrieval accuracy matter more than orchestration flexibility. You’re optimizing for correct answers, not complex multi-step reasoning.
LlamaIndex vs LangChain FAQ
How does LlamaIndex work?
LlamaIndex ingests data from sources like files, databases, and APIs, converts them into nodes, stores them in indices, and exposes query engines that fetch relevant chunks for the LLM. It focuses on retrieval, context assembly, and response synthesis rather than full application orchestration.
How does LangChain work?
LangChain provides components such as models, prompts, memory, tools, and chains that you wire together into applications. You can add agents on top so the model can decide which tool or step to run next, improving flexibility for complex tasks.
How to install LlamaIndex?
Most setups install LlamaIndex with pip install llama-index and a bit of configuration for models and embeddings. After that, you define data connectors, choose index types, and wire query engines into your application or workflow tool.
How to install LangChain?
You typically install LangChain using pip install langchain in Python or the equivalent node.js packages, then configure environment variables for your model providers. From there, you create prompts, chains, and agents in code and expose them via APIs, background workers, or n8n integrations.
What are the main use cases for LlamaIndex?
Common LlamaIndex use cases include internal documentation Q&A, legal and policy assistants, support knowledge bases, and any workflow where accurate retrieval from large document sets is more important than complex multi-step reasoning.
What is n8n LlamaIndex integration process?
To integrate LlamaIndex with n8n, you deploy LlamaIndex as a service or script, expose query endpoints, then call them from n8n workflows using HTTP nodes or code nodes. Running both on n8n hosting on Contabo keeps the data path under your control.
How to use langchain in n8n?
You can use LangChain in n8n by embedding chains or agents inside code nodes, or by hosting LangChain logic behind an HTTP endpoint and calling it from n8n. This pattern fits well when n8n handles scheduling and integrations while LangChain handles reasoning and LLM logic.
So, LangChain vs LlamaIndex in 2026: Which Should You Choose?
If your priority is rich orchestration, tools, and custom agents, LangChain is the stronger starting point. It gives you fine-grained control over prompts, tools, and chains, and pairs well with workflow engines like n8n when you need full end-to-end automation.
If your priority is grounded answers over your own data, LlamaIndex is usually the better first choice. It handles indexing, routing, and synthesis so you can focus on which sources matter, not how to stitch them together.
In many serious projects, you don’t choose only one. Teams use LlamaIndex as the retrieval and knowledge layer, LangChain as the agent and orchestration layer, and n8n as the workflow layer running on a VPS or Dedicated Server. That combination keeps costs predictable, data under your control, and engineering effort focused on solving real problems instead of constantly rebuilding the same plumbing.
When evaluating LangChain vs LlamaIndex, think about where complexity lives in your project. If it’s in multi-step reasoning and tool usage, start with LangChain. If it’s in data access and retrieval quality, start with LlamaIndex. And if it’s in both, deploy them together and let each handle what it does best.
