
Workflow automation tools offer incredible power, but most platforms ask you to trade control for convenience. When you use a cloud-only service, your data, your credentials, and your core business logic all live on someone else’s servers. For many, this is a reasonable trade-off. But for those who demand full control, absolute data privacy, and limitless scalability, there is a better path: you self-host n8n.
This guide is your complete manual for taking back control of your automation stack. We’ll walk you through every step to install n8n on VPS infrastructure, turning a standard virtual server into a powerful and private automation engine. Move beyond the constraints and escalating costs of proprietary cloud services. By running your own n8n VPS instance, you unlock a level of flexibility, security, and cost-effectiveness that is simply unmatched. From choosing the right server to securing your instance and preparing it for high-volume workflows, this is everything you need to build your own automation powerhouse.
Why Self-Host n8n? Understanding the Benefits of Full Control
Before getting into the technical how-to, it’s important to understand why you would choose to self-host n8n. The convenience of cloud services is appealing, but it comes with hidden costs and compromises. Self-hosting puts you firmly in control, delivering three core benefits that are essential for any serious user.
Drastically Lower Your n8n Cost
This is often the most immediate and tangible advantage. Cloud automation platforms typically charge per “task” or “execution.” While this may be manageable for light use, costs can increase quickly as your business grows and your workflows become more complex. A multi-step workflow that runs thousands of times a day can easily push you into expensive enterprise plans.
When you self-host n8n, you break this link between usage and cost. There are no software-imposed limits on workflows, steps, or executions. Your only recurring cost is the server infrastructure itself. This means you can scale your automation efforts to millions of executions for the price of a modest VPS, delivering an incredible return on investment.
Achieve True n8n Data Privacy
In an age of tightening data regulations, this is a serious benefit. With a cloud service, you send your sensitive data and application credentials to a third-party provider. When you self-host, your data never leaves your control. All processing happens on your own private server. For organizations in regulated fields like healthcare (HIPAA) or finance, or for any business needing n8n GDPR to comply with relevant data sovereignty laws, this is often the only viable solution.
Unlock Unlimited Customization
Cloud platforms are, by design, a one-size-fits-all solution. With a self-hosted n8n instance, you are running an open-source application that you can modify and extend at will. You can build custom integrations for your proprietary internal tools, modify the source code to fit unique requirements, and connect securely to internal resources that are firewalled from the public internet. Self-hosting transforms n8n from a simple tool into a fully extensible automation platform tailored to your needs.
Prefer the Easy Route? Install n8n in 1-Click at Contabo (free)
If you don’t want to follow the manual steps listed in this guide, you can now deploy n8n on a Contabo VPS with a single click and at no extra cost beyond your VPS plan. It’s the fastest way to get a working tunnel and a simple web UI for managing peers.
How to Install n8n?
If you want to set up a new instance with the 1-Click n8n Add-On:
- Choose your desired product on the n8n Hosting page.
- Select your preferred location and set a password (used for both the VPS and the application).
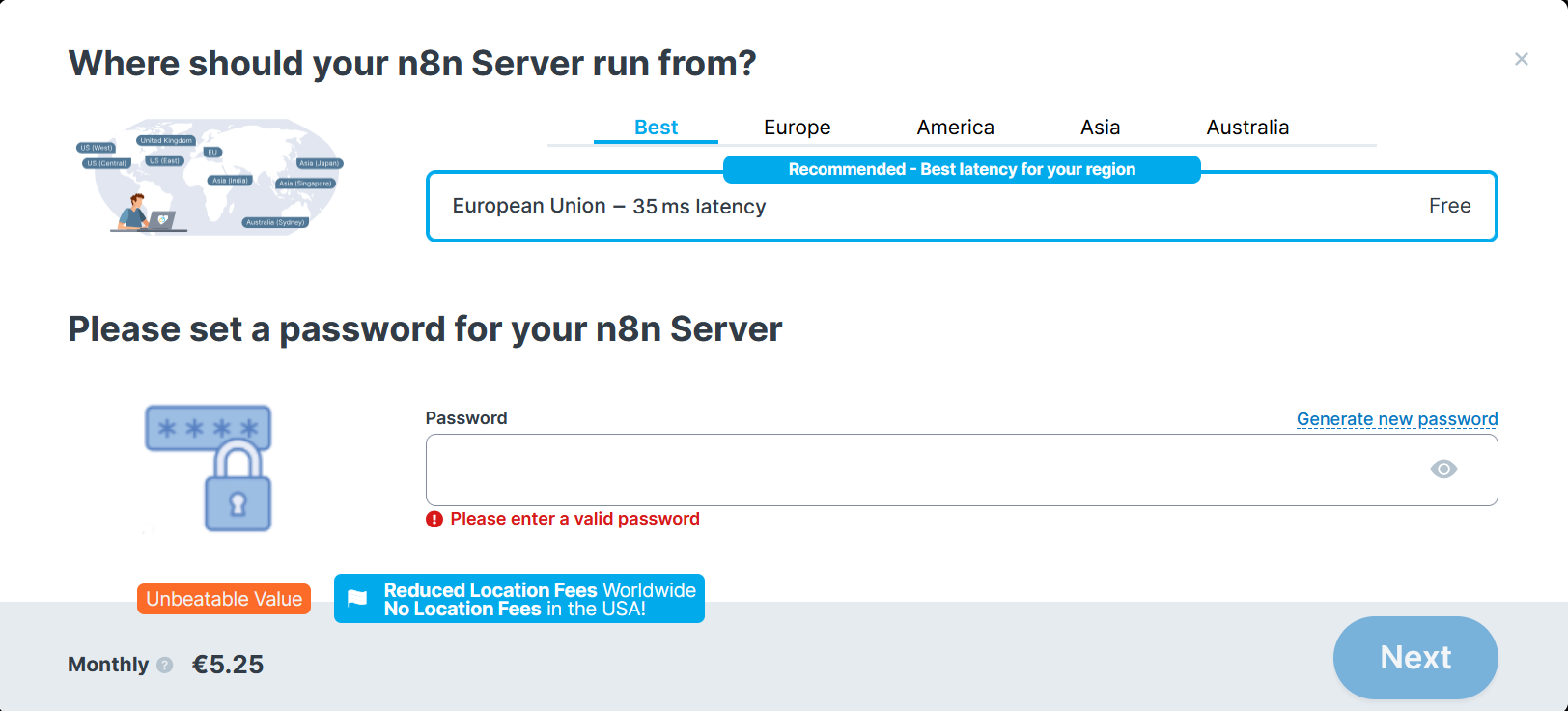
- Complete the order process.
- Log in to the Contabo Customer Control Panel and navigate to ‘VPS‘.
- Please note that it may take up to 30 minutes for your application to be installed and activated. Once it’s installed, you can access the application directly by clicking on its logo under the ‘Quick Action’ section on the right side.
If you are an existing customer and you want to run the application on an existing instance:
- In the VPS section, choose the instance you want your application to be installed on.
- Click on the three vertical dots under ‘More’, then click ‘Reinstall’.
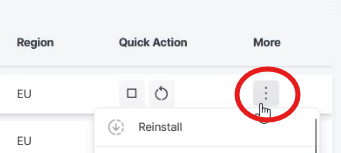
- Select your preferred installation type and configure it.
- Click ‘Install‘.
- The application button will appear under ‘Quick Action’. You can access the application directly by clicking on the icon of the application. Please note that it may take up to 30 minutes for your application to install.
Prerequisites: n8n Hardware and Software Requirements for Self-Hosting
Setting up the right environment is the first step to a smooth installation. n8n hosting requirements are flexible, but meeting the recommended specs will ensure stable and performant operation.
Hardware and VPS Recommendations
An n8n VPS provides the perfect balance of cost, performance, and scalability for self-hosting.
- Minimum: 1 vCPU, 1 GB RAM, 10 GB Disk Space
- Recommended for Production: 2 vCPUs, 4 GB RAM, 30 GB Disk Space
When choosing your VPS, prioritize fast storage. An NVMe SSD (standard with all Contabo VPS options) will provide a significant performance boost over a traditional HDD, especially for workflows that read or write a lot of data. A Contabo VPS 10 easily meets the recommended requirements, giving you plenty of headroom to start. As your usage grows, you can easily scale up to a larger plan. Don’t forget to consider your backup strategy as well – ensure you have enough space allocated for regular snapshots or off-site backups.
Software Requirements
The easiest and most reliable method for installation is using Docker. This approach simplifies setup, updates, and overall management.
The core n8n software requirements are:
- A Linux-based OS: Ubuntu 24.04 LTS is an excellent and widely supported choice, though other distributions like Debian or CentOS will also work.
- Docker and Docker Compose: These are the tools that will manage the application container. Docker runs the container itself, while Docker Compose allows you to define your n8n service and its configuration in a simple YAML file.
- A Domain or Subdomain: While not strictly required for the initial setup, you will need a domain name (or a subdomain) pointed at your VPS’s IP address to properly secure your n8n instance with an SSL certificate.
With a properly configured n8n VPS and these software tools ready, you can proceed with the installation.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Installing n8n with Docker
This n8n docker guide provides a clear path to getting your instance running using Docker Compose for a manageable and production-ready n8n server setup.
Step 1: Prepare Your Server and Install Docker
First, connect to your VPS via SSH. It’s always a good practice to update your system’s package list and upgrade existing packages.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yNext, install Docker and Docker Compose. The official convenience script is the easiest way to get the latest Docker version.
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh
sudo sh get-docker.sh
sudo apt install docker-compose-v2 -yAdd your user to the docker group to run commands without sudo. You’ll need to log out and log back in for this change to take effect.
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}Verify both installations with docker --version and docker compose version.
Step 2: Create the n8n Configuration
Organize your setup by creating a dedicated directory for n8n.
mkdir ~/n8n && cd ~/n8nInside this directory, create two files: docker-compose.yml for the service definition and .env for your secret credentials.
Create the docker-compose.yml file:
nano docker-compose.ymlPaste in the following configuration. This Docker Compose n8n setup uses a Postgres database and creates persistent volumes to safeguard your data.
version: '3.7'
services:
n8n:
image: n8nio/n8n
restart: always
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:5678:5678"
environment:
- DB_TYPE=postgresdb
- DB_POSTGRESDB_HOST=postgres
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PORT=5432
- DB_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE=${POSTGRES_DB}
- DB_POSTGRESDB_USER=${POSTGRES_USER}
- DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD=${POSTGRES_PASSWORD}
volumes:
- n8n_data:/home/node/.n8n
depends_on:
- postgres
postgres:
image: postgres:15
restart: always
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB=${POSTGRES_DB}
- POSTGRES_USER=${POSTGRES_USER}
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=${POSTGRES_PASSWORD}
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
n8n_data:
postgres_data:Now, create the .env file to securely store your database credentials.
nano .envAdd the following, replacing the placeholder password with a strong, unique one.
POSTGRES_DB=n8n
POSTGRES_USER=n8nuser
POSTGRES_PASSWORD=your_strong_password_hereStep 3: Start n8n
With the configuration in place, you can install n8n and start the services with a single command.
docker compose up -dThis command downloads the required Docker images and starts the containers in the background. You can check the status with docker compose ps. At this point, n8n is running and ready to be secured for production use. It’s a good idea to check the logs once (docker compose logs -f n8n) to ensure there were no errors during startup.
Securing Your n8n Instance with SSL and an NGINX Reverse Proxy
A critical part of any production deployment is ensuring strong n8n security. This means running your instance behind a reverse proxy and enabling SSL/TLS encryption for all traffic. We’ll use NGINX for this purpose.
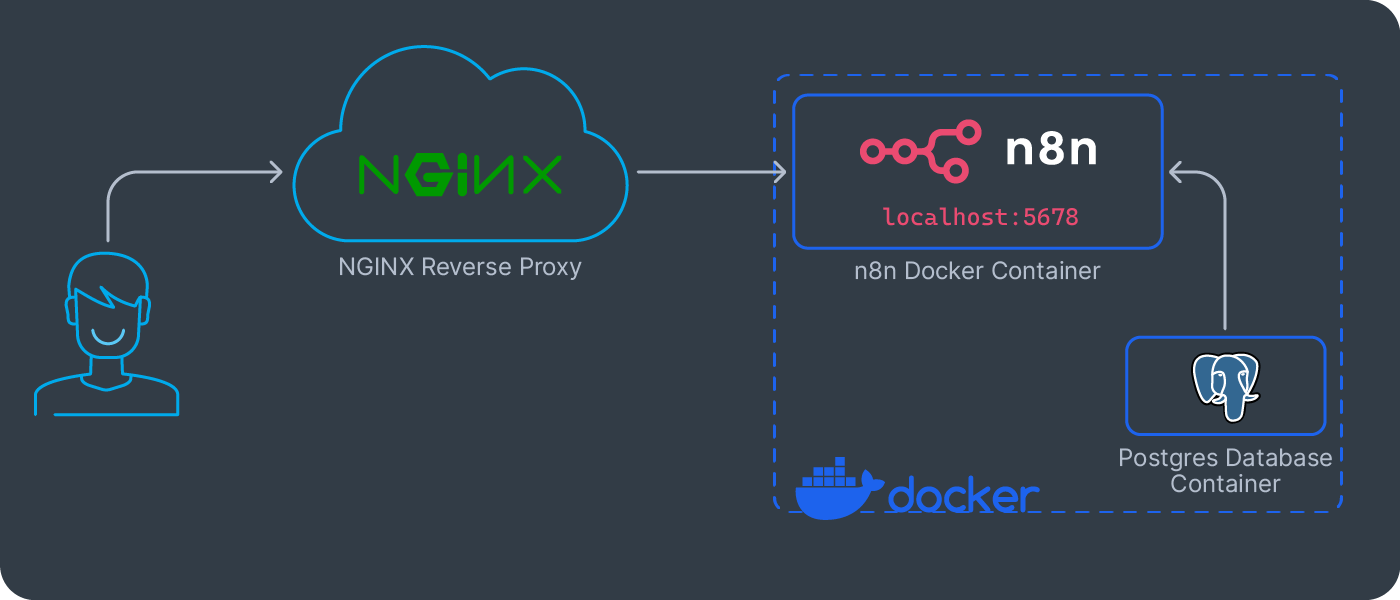
Step 1: Install and Configure NGINX
First, install NGINX on your VPS.
sudo apt install nginx -yNext, create a new NGINX server block configuration file for your n8n domain. Make sure your domain’s DNS A record is already pointing to your server’s IP address.
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/n8nPaste in the following configuration, replacing n8n.yourdomain.com with your actual domain. The settings included are optimized for n8n’s use of Server-Sent Events (SSE).
server {
listen 80;
server_name n8n.yourdomain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5678;
proxy_set_header Connection '';
proxy_http_version 1.1;
chunked_transfer_encoding off;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_cache off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}Enable this configuration by creating a symbolic link, then test and restart NGINX.
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/n8n /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginxStep 2: Enable HTTPS with Let’s Encrypt
To secure your site with an n8n SSL certificate, we’ll use the free and automated Certbot tool from the EFF.
Install Certbot and its NGINX plugin:
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -yRun Certbot to obtain and install the certificate. It will automatically detect your domain from the NGINX configuration and guide you through the process.
sudo certbot --nginx -d n8n.yourdomain.comFollow the prompts, making sure to select the option to redirect all HTTP traffic to your n8n HTTPS. Once finished, Certbot will automatically handle certificate renewals. You can now access your secure n8n instance at https://n8n.yourdomain.com.
Managing Your Self-Hosted Instance: Updates, Backups, and Logs
A running instance needs ongoing care. Proper management ensures your automation platform remains stable, secure, and reliable.
Updating n8n
Thanks to Docker, updating n8n is remarkably simple and safe. Navigate to your ~/n8n directory and run these two commands:
docker compose pull n8n
docker compose up -dThis pulls the latest version of the n8n image and recreates the container without affecting your data, which is safely stored in the persistent volume. It’s a good practice to check the n8n release notes before updating, especially for major version changes.
Implementing an n8n Backup Strategy
A regular n8n backup is not optional – it’s essential for disaster recovery. You need to back up both the n8n data volume (which holds your workflows and credentials) and the Postgres database. This can be automated with a simple shell script and a cron job. The script should stop the n8n container to ensure data consistency, perform the backups, and then restart the container. For even greater resilience, store your backups in a separate, off-site location like a cloud object storage bucket.
Accessing n8n Logs
When troubleshooting, n8n logs are your most valuable resource. You can view a live stream of the application logs with a simple Docker command from your ~/n8n directory:
docker compose logs -f n8nThis is the first place you should look when a workflow fails or the application behaves unexpectedly. For more structured n8n version control, you can also download your workflows as JSON files from the UI and commit them to a private Git repository. This allows you to track changes, collaborate with others, and easily revert to a previous version if needed.
Scaling Your n8n Setup for High-Volume Workflows
A single, powerful VPS (vertical scaling) can handle a significant number of workflows. However, when you start processing thousands of executions simultaneously or have workflows that are very resource-intensive, you may hit a ceiling. At this point, the solution is to move from vertical scaling to horizontal scaling. The key to n8n scaling is switching from the default main mode to queue mode. All n8n license models, including the free Sustainable User License, allow queue mode. This is achieved by introducing n8n Redis as a message queue.
This more advanced setup, which is detailed in the n8n documentation, is called Queue Mode. Instead of making one server bigger, you distribute the work across multiple servers, each with a specific job.
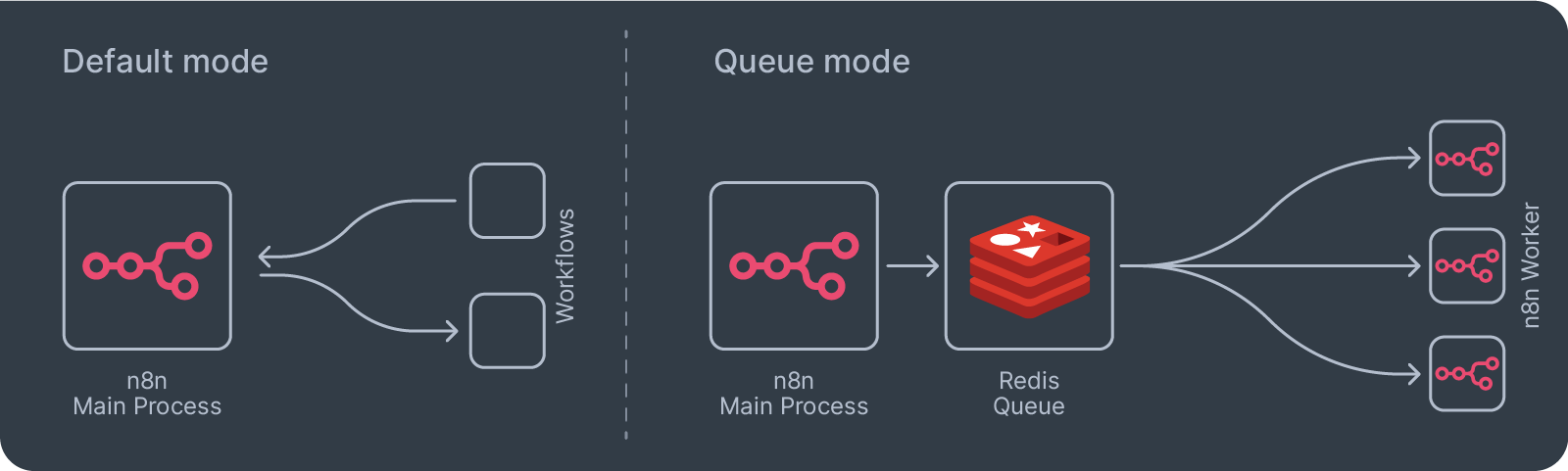
In this architecture, the main n8n process simply adds jobs to the Redis queue. Separate “worker” containers then pull jobs from the queue and execute them. This allows you to run many workflows in parallel by simply adding more worker containers, dramatically increasing your throughput and resilience. This more advanced setup, which is detailed in the n8n documentation, is the path to handling enterprise-grade workloads on your self-hosted instance. It transforms n8n from a single-process application into a distributed system capable of immense scale.
How Queue Mode Works
The standard Docker setup runs all of n8n’s processes on a single instance. Queue Mode separates these processes into a more robust and scalable architecture with three main components:
- The Main Instance: You have one (or more, for high availability) “main” n8n instance. Its job is to handle the user interface, receive incoming webhooks, and manage scheduled triggers. It does not execute the workflows itself. Instead, when a workflow is triggered, the main instance adds a job to a queue.
- The Queue (Redis): This is a high-speed message broker, typically using Redis. It acts as a waiting room for all the workflow executions that need to be run. The main instance places jobs in the queue, and worker instances pick them up from there.
- Worker Instances: These are multiple, separate n8n instances running in “worker” mode. Their only job is to connect to the queue, pick up the next available job, and execute the workflow. If you have a sudden spike of 1,000 webhook triggers, your pool of workers can process them in parallel without overwhelming the main instance.
This architecture is the standard for running n8n in a production environment with high-volume automations. While it requires more initial setup (configuring multiple Docker containers and a Redis instance), it provides a level of performance and reliability that a single-instance setup cannot match.
Troubleshooting Common n8n Self-Hosting and Docker Errors
When issues arise, a systematic approach to n8n troubleshooting will save you time. Here are a few common n8n errors.
- Permission Denied on Docker Volume: If the n8n container fails to start with a permission error in the logs, it’s likely an ownership issue on the host’s volume directory. The
nodeuser inside the container (typically UID1000) needs write access.sudo chown -R 1000:1000 /path/to/volumecan often resolve this. - Container Restart Loops: This almost always points to a configuration error, often incorrect database credentials in your
.envfile. Check the n8n Docker logs withdocker compose logs n8nto find the specific error message that occurs just before shutdown. - Network Connectivity Issues: If a workflow can’t connect to an external service, check your VPS firewall rules. If it can’t connect to another Docker container (like the database), make sure you are using the service name from your
docker-compose.yml(e.g.,postgres) as the hostname, notlocalhost.
The Self-Hosted Advantage: A Deep Dive into n8n Privacy and Customization
We’ve covered the practical steps of getting your n8n instance running, but it’s worth taking a closer look at what self-hosting truly unlocks. This goes far beyond simply running your own server – it’s about changing your relationship with your automation platform. When you self-host, you move from being a “user” to an “owner,” gaining a level of n8n privacy and n8n customization that is simply impossible with any cloud-based service.
Full Control of Your Data
In a self-hosted environment, you create a secure, isolated “black box” for your automation. Every piece of data, from your application credentials to the sensitive customer information flowing through your workflows, remains within your infrastructure. This makes a big difference for your data privacy.
- Geographic Data Sovereignty: Are your customers in the European Union? By deploying your n8n VPS in an EU-based data center, you can ensure that all data processing occurs within the geographic boundaries required for GDPR compliance. You are no longer reliant on a third-party’s data processing agreements or server locations.
- Zero Third-Party Credential Exposure: Every credential you add to a self-hosted n8n instance is encrypted and stored in your own database, on your own server. Your API keys for Stripe, your database passwords, and your private SSH keys are never transmitted to or stored by an external company. This dramatically reduces your vulnerability to common attacks and eliminates an entire class of third-party data breach risks.
- Automating in Air-Gapped Environments: For organizations with the highest security requirements, such as defense contractors, financial institutions, or research labs, n8n can be deployed in a network that is completely disconnected from the public internet. This allows you to automate internal processes between firewalled systems.
Limitless n8n Customization
The ability to modify and extend a self-hosted n8n instance is where its true potential is realized.
- Building Your Own Custom Nodes: Imagine you use a proprietary, in-house ERP system or a niche industry-specific piece of software. With cloud tools, you’d be out of luck. With self-hosted n8n, a developer on your team can use the n8n Node Development Kit to build a completely custom node. This allows you to create a first-class integration, complete with a user-friendly interface, that appears right alongside the official nodes in your n8n editor. You can turn any internal tool into a fully-fledged, automatable service.
- Extending Functionality with External Libraries: The standard Code Node in n8n is already powerful, but on a self-hosted instance, you can configure it to import external npm and Python libraries. This is a game-changer. Need to perform complex statistical analysis on a dataset? Import the
pandaslibrary. Need to generate a PDF report from workflow data? Usepdf-lib. This gives you access to the vast ecosystems of JavaScript and Python, allowing you to perform virtually any task you can imagine directly within a workflow. - Modifying the Core Application: Because you have the source code, you can change anything. Don’t like a certain UI element? You can change it. Need to add a custom logging provider that sends data to your internal platform? You can. This level of control allows you to deeply integrate n8n into your existing technology stack and operational procedures.
- Creating Branded and Embedded Experiences: For businesses looking to offer automation to their own customers, n8n’s Enterprise license allows you to white-label the editor and even embed it directly into your own SaaS application. This empowers you to provide powerful, user-friendly workflow automation capabilities as a feature of your own product, all running on your private, secure infrastructure.
This deep level of n8n customization and n8n privacy is what takes a self-hosted n8n instance from a simple workflow tool to a core piece of your business’s technology infrastructure.
Self-host n8n FAQ
Is it difficult to self-host n8n?
It requires some comfort with the Linux command line and Docker. However, by following a guide like this one, the process is straightforward for anyone with basic sysadmin skills. The initial learning curve is well worth the benefits in control and cost savings.
How much does it really cost to self-host n8n?
Your only direct cost is for the VPS. A small server can cost as little as $3-6 per month. This is significantly cheaper than the high-tier plans on cloud platforms, especially for high-volume use.
Is a self-hosted instance secure?
Yes, when configured correctly. Using a reverse proxy with SSL, maintaining a firewall, and keeping your system updated are essential practices. A well-managed self-hosted instance gives you more security because you have full control over the entire environment.
How do I handle updates without breaking my workflows?
The recommended Docker-based setup makes updates very safe. Because your data is stored in a persistent volume, updating the n8n application container is a non-destructive process. Best practice is to test the new version in a staging environment before upgrading your production instance.
What about multi-user support?
The open-source version of n8n has basic user management. For more advanced features like role-based access control (RBAC) and SSO, n8n offers an Enterprise license for self-hosted instances.
