
What is a Subdomain
Subdomains are an essential tool for organizing website content, especially when you need to separate sections like blogs, online stores, or customer support under a single domain. A subdomain not only helps streamline your website, but it also plays a significant role in SEO and overall user experience. In this guide, we’ll explain what a subdomain is, outline the best practices for subdomain setup, and walk you through how to create a subdomain on hosting platforms like Contabo. We’ll also dive into crucial SEO considerations, such as performing a subdomain lookup, configuring subdomain DNS settings, and comparing domain vs subdomain usage for your website.
Subdomain Examples
Subdomains can be used to organize and separate content into clear, navigable sections. Here are some common examples of subdomains:
- blog.example.com: Used to host a blog that is distinct from the main business site.
- shop.example.com: A subdomain dedicated to an online store.
- support.example.com: A subdomain specifically for customer service or FAQs.
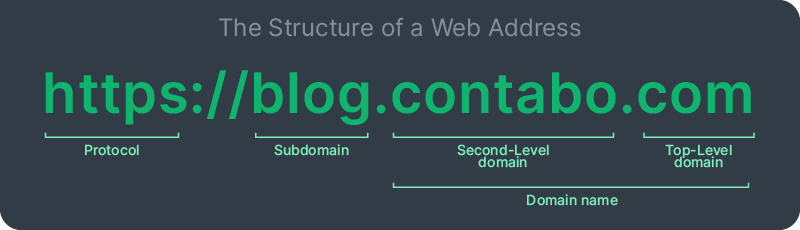
Subdomains improve the structure of your website and help ensure that each section is tailored to specific audiences or purposes. Additionally, performing a subdomain lookup is crucial to ensure proper setup in your DNS records and to maintain functionality.
Benefits of Using Subdomains
- Better Content Organization: Subdomains help separate your website into distinct sections. For example, support.example.com can focus on customer service, while the main site (example.com) handles product information. This allows for better content organization and easier navigation for users.
- SEO Flexibility: Since Google treats subdomains as separate sites, you can target specific keywords on subdomains without affecting the SEO of the main domain. However, keep in mind that in a domain vs subdomain comparison, each subdomain requires its own SEO strategy and optimization efforts.
- User Experience Improvement: Subdomains create a clear separation between different services or products, enhancing navigation and usability. According to John Mueller from Google, search engines initially treat subdomains separately, but after a few days, they integrate well into the overall site structure, providing a seamless user experience.
How to Set Up a Subdomain
Contabo offers several control panel options for managing your hosting services, including Plesk, Webmin, and cPanel. These control panels provide user-friendly interfaces to handle various aspects of your hosting account, including domain and subdomain management. Whether you’re using Plesk, Webmin, or cPanel, the process is straightforward. While specific steps may vary slightly depending on the control panel, here’s a general guide on how to create a subdomain on Contabo:
Log in to your Contabo account and access the customer control panel at https://my.contabo.com.
- Navigate to the “DNS Zone Management” section.
- Click on “Add Record” to create a new DNS entry.
- Choose the type of record you want to create. For a subdomain, you’ll typically use a CNAME record.
- Enter the subdomain name you want to create (e.g., “blog” for blog.yourdomain.com).
- In the value field, enter the endpoint URL where you want the subdomain to point. This could be your Contabo Object Storage bucket URL (for hosting a static website) or another IP address or domain.
- Save the changes.
- Wait for the DNS changes to propagate, which can take anywhere from a few minutes to 48 hours.
If you’re setting up a subdomain for a static website hosted on Contabo Object Storage:
- Upload your website files to your Object Storage bucket.
- Configure the bucket for website hosting.
- Set the appropriate file permissions (usually public read access).
- Use the bucket’s endpoint URL as the value for your CNAME record in the DNS settings.
Subdomain vs. Subdirectory: Key Differences
The primary difference between subdomains and subdirectories lies in how search engines like Google treat them. A subdomain (e.g., app.example.com) is considered a separate site from the main domain, allowing for independent content and SEO strategies. In contrast, a subdirectory (e.g., example.com/app) is treated as part of the main domain, meaning it shares the overall SEO efforts and authority of the primary site.
| Feature | Subdomain | Subdirectory |
| URL Structure | blog.example.com | example.com/blog |
| Content Separation | Completely separate site | Part of the main domain |
| SEO Impact | Treated as separate by Google | Shares SEO with the main site |
| Use Case | Good for large projects like blogs or eCommerce | Preferred for simpler websites |
When to Use Subdomains:
Subdomains are ideal for separating content that differs from your main website, such as a blog, online store, or customer support section. They are particularly useful for content that needs to function independently from the main domain, such as an e-commerce store targeting specific keywords, or a tool or service that requires its own dedicated space. Subdomains help ensure that each section of your website is tailored to its specific purpose while remaining connected to the overall domain structure.
Uses of Subdomains with Pros and Cons
| Use Case | Pros | Cons |
| Content Organization | – Improves navigation and user experience – Allows for distinct content sections | – Requires more resources to manage – Can complicate site structure |
| Marketing Campaigns | – Enables targeted campaign pages – Allows for separate tracking | – May not build long-term SEO value – Requires additional setup |
| Localization | – Tailors content for specific regions/languages – Improves local search visibility | – Increases content management complexity – Can dilute overall domain authority |
| Development/Testing | – Provides isolated testing environment – Prevents impact on live site | – May accidentally become public – Requires careful access management |
| E-commerce | – Separates store from main site – Allows for specialized e-commerce features | – Splits traffic and analytics – May complicate cross-site user experience |
| Mobile Site | – Optimizes experience for mobile users – Can improve mobile search rankings | – Requires separate maintenance – Potential for duplicate content issues |
| Blog | – Allows for distinct blog design/functionality – Can target different keywords | – May not contribute to main domain’s SEO – Complicates content strategy |
| Support/Knowledge Base | – Organizes support content separately – Can improve customer service efficiency | – May isolate support content from main site – Requires additional navigation planning |
| Multitenancy | – Enables hosting multiple clients/brands – Provides customization for each tenant | – Increases hosting complexity – Can lead to security concerns if not managed properly |
| API/Developer Resources | – Separates technical content – Improves developer experience | – May limit integration with main site content – Requires additional documentation management |
Conclusion
Subdomains are a valuable tool for organizing and managing large websites under a single domain, enhancing user experience by providing dedicated spaces for sections like blogs, online stores, or customer support. Setting up subdomains on platforms like Contabo requires careful attention to DNS settings and SEO optimization to ensure seamless performance. Whether you’re deciding between using a domain or subdomain, or assessing the SEO impact, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits and challenges for your website’s structure and growth.
Ready to optimize your website with subdomains? Contabo offers user-friendly control panels like Plesk, Webmin, and cPanel, making it easy to create and manage subdomains. Explore Contabo’s hosting plans and get started today!
