
When you type a web address into your browser, have you ever wondered how it finds the website you’re looking for? Nameservers play a key role in this process. This guide will explain what nameservers are, why they matter, and how they work in domain management.
What Are Nameservers?
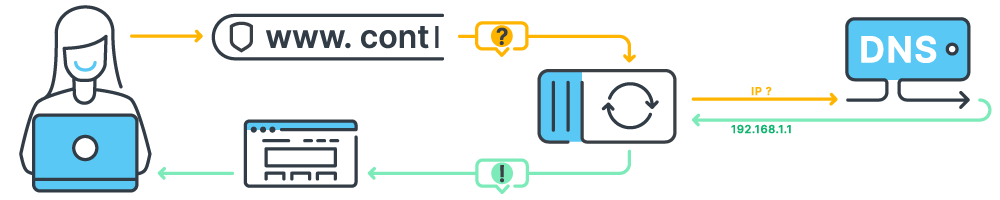
Nameservers are part of the Domain Name System (DNS). They work like the internet’s address book, turning easy-to-remember domain names (like www.contabo.com) into IP addresses that computers use.
Here’s how it works:
- You enter a domain name in your browser.
- Your computer asks a DNS resolver to find the IP address.
- The resolver checks with the nameservers for that domain.
- The nameservers provide the right IP address.
- Your browser connects to that IP address and loads the website.
Nameservers usually come in pairs for backup. You might see them as ns1.example.com and ns2.example.com. They hold DNS records that link domain names to IP addresses and other details.
Why Do Nameservers Matter?
Nameservers are important for several reasons:
- They let us use simple domain names instead of hard-to-remember IP addresses.
- They can spread traffic across servers, helping websites run smoothly.
- Having multiple nameservers keeps sites accessible if one server has problems.
- They make sure emails reach the right place.
- They can add extra security to protect against some online threats.
- They allow you to change web hosts without changing your domain name.
For website owners, well-set-up nameservers help keep your online presence stable and accessible.
What Do Nameservers Do for Domain Names?
For domain names, nameservers connect your domain to your web hosting. They tell the internet where to find information about your domain, including your website files and email settings.
Nameservers handle these tasks for your domain:
- Point to Your Web Host: They direct visitors to the server where your website lives.
- Manage DNS Records: They store different types of information:
- A records for your website’s IP address
- MX records for email routing
- CNAME records for subdomains
- TXT records for domain verification
- Enable Host Changes: You can switch web hosts by updating nameservers, without moving your domain.
- Handle Multiple Domains: One set of nameservers can manage several domains, making things simpler.
When you first register a domain, you’ll usually use the registrar’s nameservers. But when you set up web hosting, you’ll often need to update these to your host’s nameservers.
Types of DNS Records
Understanding different DNS record types is important for managing your domain effectively, and nameservers play a key role in storing and serving these records. When you configure your nameservers, you’re essentially telling them which DNS records to use for your domain. Here are the main types of DNS records that nameservers handle:
| Record Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| A | Maps a domain to an IPv4 address | example.com -> 192.0.2.1 |
| AAAA | Maps a domain to an IPv6 address | example.com -> 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 |
| CNAME | Creates an alias from one domain to another | www.example.com -> example.com |
| MX | Specifies mail servers for handling email | example.com -> mail.server.com |
| TXT | Stores text information for various purposes, like domain verification | example.com -> “v=spf1 include:_spf.example.com ~all” |
| NS | Identifies the nameservers for the domain | example.com -> ns1.example.com |
| SOA | Provides authoritative information about a DNS zone | example.com -> 20220101 3600 1800 604800 86400 |
Nameservers store these records and respond to queries about your domain using this information. For example, when someone tries to visit your website, your nameservers will provide the A or AAAA record to direct them to the correct IP address. Similarly, when an email is sent to your domain, the nameservers will provide the MX record to ensure the message reaches the right mail server.
By understanding these record types and how nameservers use them, you can more effectively manage your domain’s DNS settings and troubleshoot any issues that arise.
How to Check Nameservers
Checking your domain’s nameservers is straightforward. Here are some ways to do it:
- WHOIS Lookup:
- Go to a WHOIS lookup site (like whois.icann.org)
- Type in your domain name
- Find the “Name Server” or “Nameservers” section
- Command Line (Windows/Mac/Linux):
- Open Command Prompt or Terminal
- Type
nslookup -type=ns yourdomain.com - Press Enter to see the nameservers
- Online DNS Tools:
- Use a service like DNSChecker.org
- Enter your domain and choose “NS” record type
- Domain Registrar Dashboard:
- Log into your domain registrar account
- Go to your domain’s DNS settings
- Look for the nameserver information
Checking your nameservers regularly helps you spot and fix any DNS-related issues quickly.
How Nameservers Work with Your VPS
Whether you’re using a Virtual Private Server (VPS), Virtual Dedicated Server (VDS), or Dedicated Server, nameservers are essential for connecting your domain to your server. Here’s the process:
- When you set up your VPS, you’re assigned an IP address.
- You create an A record in your DNS settings that points your domain to this IP address.
- Your nameservers store this A record.
- When someone visits your domain, the nameservers provide the IP address of your VPS.
This setup allows you to host multiple websites on a single VPS, each with its own domain name. It’s an efficient way to manage your online presence, especially for small to medium-sized businesses or personal projects.
Managing Your Domains using Nameservers via the Customer Control Panel
When you want to manage your domain’s DNS settings through the Customer Control Panel (CCP), you’ll need to change your domain’s nameservers. This process tells your domain registrar to use Contabo nameservers for DNS resolution, giving you full control over your domain’s DNS records through the CCP. Before changing your nameservers, it’s necessary to set up a DNS zone in your Contabo CCP. Registrars typically check for the existence of this zone when processing a nameserver change request. Here’s how to prepare and implement the change:
- Create a DNS Zone in the CCP:
- Log in to your Contabo Customer Control Panel
- Navigate to the DNS Management section
- Create a new DNS zone for your domain
- Add necessary DNS records (A, CNAME, MX, etc.) as needed
- Gather Nameserver Information:
Contabo provides three nameservers:- ns1.contabo.net
- ns2.contabo.net
- ns3.contabo.net
- Update Nameservers at Your Domain Registrar:
- Log in to your domain registrar’s website
- Locate the nameserver settings for your domain
- Replace the current nameservers with Contabo nameservers
- Save the changes
- Wait for Propagation:
- Nameserver changes can take 24-48 hours to propagate globally
- During this time, you may experience intermittent issues with your domain
- Verify the Change:
- Use online DNS lookup tools to check if your domain is using Contabo nameservers
- Ensure your website and email services are functioning correctly
By changing your nameservers to Contabo versions, you gain several advantages:
- Centralized management of your DNS records through the Contabo CCP
- Access to reliable and fast DNS infrastructure
- Easier integration with other Contabo services you may be using
The Role of Nameservers in Website Performance
Nameservers can significantly impact your website’s performance in several ways:
- Response Time: Fast nameservers reduce the time it takes for visitors to reach your site.
- Reliability: Multiple nameservers ensure your site remains accessible even if one fails.
- Geo-Location: Some DNS providers offer nameservers in different geographic locations, potentially reducing latency for global visitors.
- Load Balancing: Advanced DNS configurations can distribute traffic across multiple servers, improving site performance during high-traffic periods.
Common Issues and Solutions
Even with proper setup, you might run into nameserver-related problems. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
- Slow Website Loading: This could be due to slow nameservers. Try using a DNS speed test tool to check your nameserver response times.
- Website Not Accessible: If your site is down, check if your nameservers are set correctly. Verify them using the methods we described earlier.
- Email Delivery Problems: Incorrect MX records can cause email issues. Check that your MX records are properly set in your DNS settings.
- Nameserver Update Delays: Changes to nameservers can take up to 48 hours to spread worldwide. Be patient and check again after this time.
- Mismatched Nameservers: Make sure the nameservers listed with your domain registrar match those provided by your hosting company.
Nameserver Security
Securing your nameservers is vital for protecting your online presence. Here are some key security measures:
- DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions): This protocol adds a layer of security to DNS queries and responses, helping prevent DNS spoofing attacks.
- Registrar Lock: This feature prevents unauthorized changes to your domain’s nameservers.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Enable this on your domain registrar and hosting accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep an eye on your DNS settings and nameserver configurations for any unexpected changes.
Implementing these measures can significantly enhance the security of your domain and nameservers.
Future Developments
As the internet evolves, so do nameservers and DNS:
- DNS over HTTPS (DoH): This protocol encrypts DNS queries, enhancing privacy and security.
- Anycast DNS: This technology improves DNS resolution speed and reliability by routing queries to the nearest server.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies may be used to optimize DNS routing and improve performance.
- IoT Integration: As more devices connect to the internet, DNS will play an essential role in managing these connections.
Staying informed about these developments can help you make better decisions about your domain and hosting management.
Conclusion
Nameservers play a vital part in how the internet works, connecting domain names to IP addresses and making sure your website is accessible to visitors. Understanding how they work and how to manage them helps you maintain your online presence effectively.
Whether you’re starting a new website or managing an existing one, setting up your nameservers correctly is key. Contabo provides reliable nameservers and user-friendly DNS management tools through the Customer Control Panel to help ensure your domain points where you want it to.
By understanding nameservers and DNS, you’re better equipped to manage your online presence, troubleshoot issues, and make informed decisions about your hosting and domain management.
