Choosing the right email protocol can significantly impact how you manage and access your emails. IMAP and POP3 are two widely used email retrieval protocols, each with unique benefits and limitations. Understanding their differences can help you select the best protocol for your personal, business, or self-hosted email needs. For Contabo users, especially those using VPS or dedicated servers, understanding these protocols is key to setting up an effective email server.
What is IMAP?
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) is an email retrieval protocol. It lets you access and manage emails directly on the server. This setup provides real-time synchronization across multiple devices.
Key Feautes
- Emails are stored on the server, not downloaded to the device.
- Synchronizes email status (read, unread, etc.) across all devices.
- Organizes emails into server-based folders.
- Downloads only the email headers initially, saving bandwidth.
- Current version: IMAP4.
IMAP Best Use Cases
The email protocol IMAP is designed for users who need flexibility and accessibility in managing their emails. By keeping emails on the server, IMAP ensures that messages and their statuses are consistent across all devices. Here is why:
- Multiple Device Access: Perfect for users needing to access their emails from smartphones, tablets, and computers, allowing seamless transitions between devices.
- Limited Local Storage: Ideal for users with limited device storage who prefer keeping emails on the server to avoid using up local space.
- Real-Time Synchronization: For those who need their email status to sync across all devices, ensuring that actions like reading or deleting emails are reflected everywhere.
- Business Environments: Suitable for employees who access emails from different locations or devices, ensuring they have the most up-to-date information.
Who Should Use IMAP
IMAP is the tool of choice for individuals and organizations that require consistent, accessible, and flexible email management. Here’s who benefits the most from IMAP and the reasons why:
- Mobile Professionals: Those who frequently switch between devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, benefit from IMAP because it synchronizes emails across all connected devices. An email read or responded to on one device will reflect the same status on all others. Because the information is always available and updated on the most recent device connected, mobile professionals can work seamlessly from anywhere.
- Businesses with Remote or Distributed Teams: In business environments where employees need to access their emails from various locations or devices, IMAP ensures that everyone has the most current view of their inbox. Teams can rely on consistent, server-based email storage, facilitating collaboration and communication without the risk of missing important updates.
- Users with Multiple Devices: People who use a mix of devices—like a desktop at work, a laptop at home, and a smartphone on the go—prefer IMAP for its ability to provide a unified and synchronized email experience across all platforms. This consistency allows users to organize, respond to, and manage emails effectively, no matter which device they use.
- People Who Prefer Server Storage for Backup: IMAP is ideal for users who wish to keep their emails stored on the server rather than locally. This server-based storage acts as a backup, reducing the risk of data loss due to device failure and ensuring that emails can be accessed from any device connected to the account.
What is POP3?
POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) is a simpler email retrieval protocol that downloads emails from the server to a single device and usually deletes them from the server after download.
- Key Features:
- Emails are downloaded to the local device.
- Suitable for use on a single device.
- Allows offline access to downloaded emails.
- Simple to set up and use.
- Current version: POP3.
POP3 Best Use Cases
The email protocol POP3 is tailored for users who prefer to have their emails stored locally on a single device. It offers straightforward email management without the need for constant internet connectivity. Here is why:
- Single Device Access: Ideal for users who primarily check emails from one device, such as a desktop computer, where emails are downloaded and stored locally for convenient access.
- Offline Access: Perfect for those needing access to their emails without an internet connection, as emails are available locally once downloaded.
- Limited Server Storage: Suitable for users with email providers that offer limited server storage, allowing them to download emails to their device and free up space on the server.
- Privacy Concerns: Beneficial for individuals who prefer storing emails locally on their device rather than on a remote server, enhancing privacy and control over their data.
Who Should Use POP3
POP3 is well-suited for users who value offline accessibility, local storage, and simplicity in their email management. Here’s who should consider using POP3 and the reasons why:
- Users with Unreliable Internet: POP3 is advantageous for those who need offline access to their emails due to an unreliable or intermittent internet connection. Since emails are downloaded and stored locally, users can access their messages anytime, even without an active internet connection.
- Privacy-Conscious Users: People who prefer keeping their emails stored locally rather than on a remote server may opt for POP3. This protocol ensures that emails are downloaded to the device, providing greater control over data privacy and reducing concerns about server security.
- Users with Limited Server Storage: Individuals who want to free up space on their email server can benefit from POP3. By downloading emails to their device, they can manage server storage more effectively, ensuring that server limits do not interfere with their email usage.
- Single Device Users: POP3 is best suited for users who primarily use one device for email access. By downloading emails directly to this device, they can organize and manage their inbox without the need for synchronization across multiple platforms.
Webmail Accounts vs. Email Apps
- Webmail (e.g., Gmail, Yahoo Mail): Accessed through a web browser. Typically uses IMAP for syncing emails across devices.
- Email Apps (e.g., Outlook, Thunderbird): Can use either IMAP or POP3, depending on configuration. IMAP syncs emails across devices, while POP3 stores them locally on one device.
Differences Between POP3 and IMAP
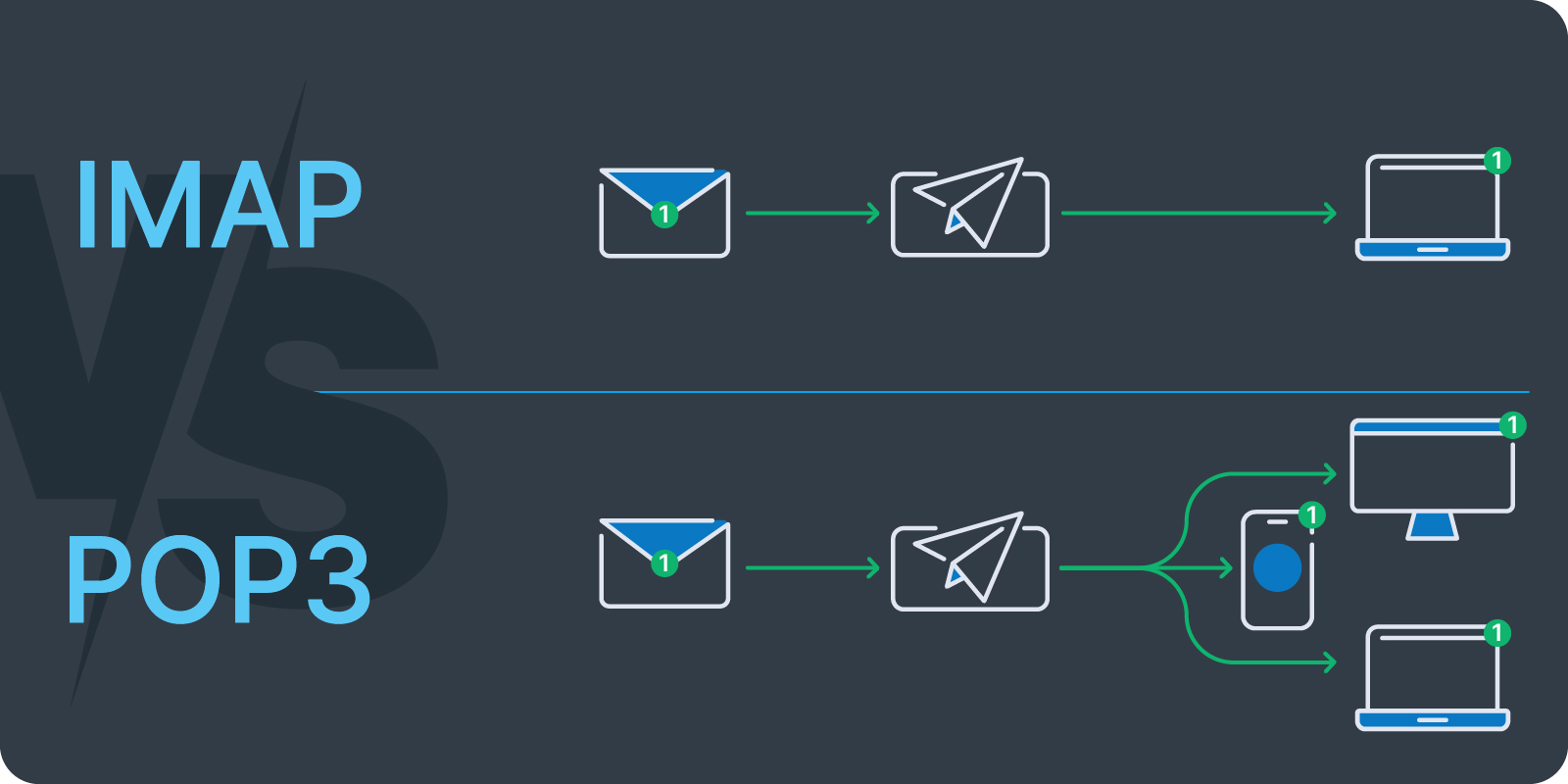
While both IMAP and POP3 are protocols for retrieving emails, they operate in fundamentally different ways. IMAP offers real-time synchronization and multi-device access, while POP3 is designed for local storage and offline access on a single device. Here’s a breakdown of their key differences:
| Feature | IMAP | POP3 |
| Email Storage | Stored on the server | Downloaded to the local device |
| Multi-Device Access | Yes, with real-time synchronization | No, limited to one device |
| Synchronization | Changes sync across all devices | No synchronization |
| Offline Access | Requires internet, limited to cached content | Full access to downloaded emails |
| Server Storage | Higher server storage required | Minimal server storage needed |
| Organization | Allows server-side email organization | Limited organization capabilities |
| Bandwidth Usage | Lower, only syncs changes | Higher due to full downloads |
| Security | Supports encryption and MFA but depends on server | Less secure, vulnerable to local threats |
Which Email Protocol Should You Choose?
The choice between IMAP and POP3 depends on your specific needs:
Choose IMAP if:
- You access your email from multiple devices.
- You need real-time synchronization.
- You prefer server-based email organization.
- You have a stable internet connection.
Choose POP3 if:
- You use a single device for email access.
- You need offline access to all your emails.
- You have limited server storage.
- You deal with unreliable or limited internet connectivity.
Security Considerations
Both IMAP and POP3 have inherent vulnerabilities, but proper configurations and additional protective measures can improve their security. Here’s how you can secure each protocol:
IMAP
- Encryption and Authentication: IMAP can use TLS (Transport Layer Security) encryption to secure the data transmitted between the client and server. Enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, ensuring that only authorized users can access the email account.
- Server Security: Since IMAP stores emails on the server, server security is crucial. This includes implementing strong password policies, regularly updating server software, and using firewalls to prevent unauthorized access. Organizations should also consider using spam and malware filtering to reduce the risk of malicious content being stored on the server.
POP3
- Local Privacy and Risks: POP3 offers local privacy by storing emails directly on the user’s device, reducing exposure to server-based threats. However, this also increases the risk if the device becomes compromised. Anyone with access to the device could retrieve sensitive emails stored locally.
- Device-Level Security: To secure POP3, additional measures at the device level are necessary. This might include:
- Encryption: Encrypting the device’s storage helps protect emails in case of loss or theft.
- Local Firewall: Implementing a local firewall can prevent unauthorized access to the device, adding an extra layer of security.
- Remote Deletion Protocols: For devices that handle sensitive information, consider enabling remote wipe capabilities. This allows emails and other data to be erased remotely if the device is lost or compromised.
- Secure Connections: Use SSL/TLS encryption for the POP3 connection to protect emails during the transfer from the server to the local device.
Both protocols require thoughtful security measures tailored to their operational differences. While IMAP relies on strong server security, POP3 demands robust device security to ensure emails remain protected.
Contabo Offerings for IMAP and POP3
For users looking to set up IMAP and POP3 email servers, Contabo offers a range of self-managed solutions. These services aren’t pre-configured out of the box, but they give you the flexibility and freedom to set up and manage your email environment according to your needs:
- Ideal for hosting self-managed email servers with IMAP and POP3 capabilities.
- Offers flexibility and control for configuring email protocols.
- Suitable for small to medium-sized businesses or individuals with moderate email traffic.
- A more powerful option than a standard VPS, offering dedicated resources within a virtual environment.
- Perfect for users who need higher performance for their email servers.
- Suitable for businesses with higher email volumes or those requiring more robust configurations.
- Best for users managing large volumes of email or multiple domains.
- Provides complete control over the server environment and maximum resources.
- Ideal for large organizations or email service providers requiring a high-performance, self-managed email solution.
With Contabo’s range of server options, you have the freedom to customize and manage your email server setup, ensuring it fits your specific requirements.
Conclusion
IMAP suits users who need access to their emails across multiple devices with real-time synchronization, while POP3 works best for those who use a single device and require offline access. For Contabo users, the choice between these protocols—and the appropriate server type—depends on factors like email volume, the number of accounts, storage requirements, and the level of control desired. Contabo offers flexible solutions, including VPS, VDS, and dedicated servers, allowing users to set up and manage secure email servers tailored to both personal and business needs.
