
As your small business grows, so do your IT needs. Maybe you’ve outgrown your current setup, or perhaps you’re looking to upgrade from that server humming away in your office closet. Whatever brings you here, you’re facing an important choice: should you move to the cloud or consider colocation for your IT infrastructure?
Think of this decision like choosing between renting a fully furnished apartment (cloud) or leasing space in a secure building to set up your own furniture (colocation). Both options get you out of managing everything at home, but they come with different levels of control, responsibility, and cost.
In this guide, you’ll learn exactly what cloud and colocation options mean for your business, their real costs and benefits, and how to choose the solution that best fits your needs. No technical jargon – just clear, practical information to help you make an informed decision.
Let’s start by understanding exactly what cloud hosting means for your business.
Article Topics
- What is Cloud Hosting?
- What is Colocation Hosting?
- Cloud vs Colocation: Key Differences
- Pros and Cons: Cloud vs Colocation for Small Businesses
- Cost Comparison: Cloud vs Colocation
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud vs Colocation
- Security Considerations: Which is More Secure?
- Performance and Reliability: Cloud vs Colocation
- How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business
- Real-World Use Cases: Cloud and Colocation in Small Businesses
- Conclusion: Which is Best for Your Small Business?
What is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting might sound complex, but it’s actually a straightforward concept. It’s like a virtual workspace where you can access all your IT resources over the internet, without worrying about physical hardware.
How Cloud Hosting Works
When you choose cloud hosting, you’re essentially renting computing power and storage from a provider’s vast network of servers. Instead of buying and maintaining your own hardware, you get access to resources that can grow or shrink based on your needs. Whether you need a simple Virtual Private Server (VPS) for your website or a more powerful Virtual Dedicated Server (VDS) for running business applications, the cloud makes it possible.
Types of Cloud Solutions
Public cloud services work like a shared office space – you get your own secure area within a larger shared environment. It’s cost-effective and perfect for many small businesses.
Private cloud offers a more exclusive setup, like having your own office building. While it costs more, it gives you complete control over your environment.
Hybrid solutions combine both approaches, letting you keep sensitive data in a private cloud while using public cloud resources for everything else.
Basic Components
Cloud hosting typically includes:
- Computing power for running your applications
- Storage for your data
- Network resources for connectivity
- Security features to protect your business
- Management tools to control it all
The beauty of cloud hosting lies in its simplicity – you focus on using these resources while your provider handles the technical details.
Next, let’s explore colocation to understand how it differs from cloud hosting.
What is Colocation Hosting?
Think of colocation like storing and running your servers in a high-tech hotel. You own the equipment, but instead of keeping it in your office, you rent space in a specialized data center that provides the perfect environment for your hardware to operate.
How Colocation Works
When you choose colocation, you get dedicated server rack space in a professional data center infrastructure. The facility provides essential services like power, cooling, physical security, and internet connectivity.
What’s Included
A typical colocation setup provides:
- Secure physical space for your servers
- Reliable power with backup systems
- Climate control to protect your equipment
- High-speed internet connectivity
- Physical security and access control
- Basic hands-on support when needed
Your Responsibilities
Unlike cloud hosting, with colocation you’re in charge of your own hardware. This means you’ll need to:
- Purchase and own your servers
- Handle hardware maintenance and updates
- Manage your operating systems and applications
- Plan for hardware replacements and upgrades
This level of control can be perfect for businesses that need specific hardware configurations or want to maintain complete oversight of their infrastructure.
Let’s explore how these differences between cloud and colocation hosting affect your business decisions.
Cloud vs Colocation: Key Differences
Let’s break down the main differences between cloud and colocation to help you understand which might work better for your business.
| Feature | Cloud | Colocation |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low (monthly fees) | High (hardware purchase) |
| Ongoing Costs | Usage-based, variable | Fixed rack space + utilities |
| Control Level | Limited hardware control | Full hardware control |
| Management Needs | Provider handles most tasks | Self-managed hardware |
| Scalability | Instant, flexible | Requires hardware planning |
| Technical Expertise | Basic knowledge needed | Advanced skills required |
Infrastructure Control
With cloud hosting, you’re using someone else’s infrastructure – like renting a furnished apartment where everything is set up for you. You get flexibility but less control over the underlying hardware.
In colocation, you own and control your hardware – similar to owning your furniture but placing it in a managed space. This gives you complete control over your infrastructure but requires more hands-on management.
Cost Structure
Cloud services typically follow a pay-as-you-go model. You’ll see monthly bills based on your actual usage, making costs predictable but potentially variable.
Colocation involves bigger upfront costs for hardware but can offer more predictable long-term expenses. You’ll pay a fixed rate for your rack space and power usage, plus your own hardware maintenance costs.
Management Responsibilities
Cloud providers handle most infrastructure management tasks. Your team focuses on using the resources rather than maintaining them.
With colocation, you’re responsible for your hardware and software management. The facility handles environmental factors like power and cooling, but server maintenance is up to you.
Understanding these differences helps set realistic expectations for each option. Next, let’s look at specific advantages and challenges of cloud hosting for small businesses.
Pros and Cons: Cloud vs Colocation for Small Businesses
Let’s compare how each solution might help or challenge your business operations.
Cloud Solutions
Advantages:
Quick to Get Started
No need to wait for hardware delivery or setup. Sign up for a VPS or VDS, and you can have your environment running in minutes rather than weeks.
Predictable Monthly Costs
Instead of large upfront investments, you pay monthly based on what you use. This makes budgeting more straightforward and helps manage cash flow.
Built-in Support
Most cloud services include technical support and infrastructure management, letting you focus on your business rather than IT maintenance.
Challenges:
- Limited hardware control for specialized applications
- Costs can increase with unexpected resource usage
- Complete dependency on internet connectivity
Colocation Solutions
Advantages:
Complete Hardware Control
Choose and own your equipment, giving you freedom to use specific server configurations that match your exact needs.
Professional Infrastructure
Get enterprise-grade power, cooling, and connectivity without building your own data center. Your hardware lives in an environment designed to protect it.
Predictable Long-term Costs
While initial investments are higher, monthly colocation fees typically stay consistent, making long-term budgeting easier.
Challenges:
- Significant upfront hardware investment
- Requires technical expertise for management
- Physical access needs consideration
Next, let’s compare the actual costs of each option.
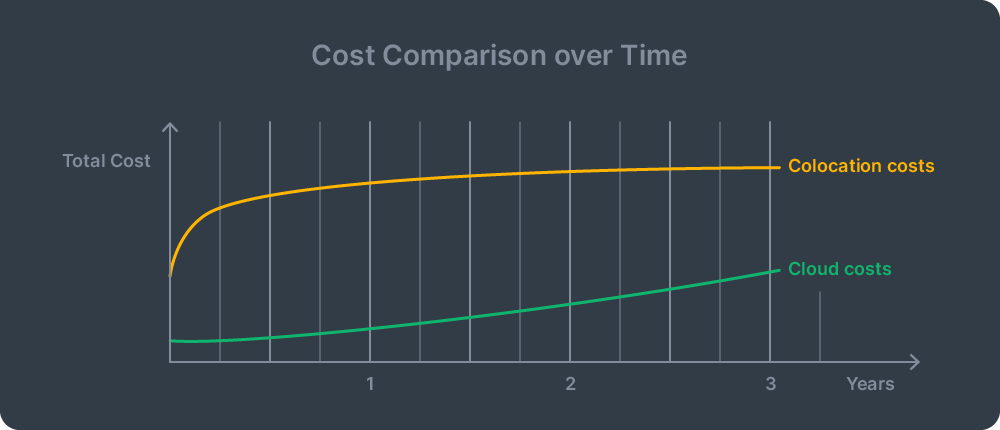
Cost Comparison: Cloud vs Colocation
Understanding the true costs of each option helps you make a financially sound decision for your business. Let’s break down the different cost factors and see how they compare over time.
Cloud Hosting Costs
With cloud hosting, your primary expenses are operational. You’ll pay for:
- Monthly resource usage (CPU, memory, storage)
- Data transfer fees
- Additional services like backups or monitoring
- Optional managed services
The beauty of cost-per-usage pricing is that you only pay for what you need. Starting costs can be as low as a few dollars per month for basic VPS solutions, scaling up as your requirements grow.
Colocation Costs
Colocation involves both capital and operational expenses:
Initial Costs:
- Server hardware
- Networking equipment
- Installation and setup
Monthly Costs:
- Rack space rental
- Power consumption
- Network bandwidth
- Remote hands support when needed
Long-term Cost Considerations
While cloud often starts cheaper, colocation can become more cost-effective over time for predictable workloads. The key is understanding your growth trajectory and resource needs.
Consider factors like:
- Expected growth rate
- Hardware refresh cycles
- Staff training and management
- Backup and disaster recovery needs
Next, let’s examine how each option handles growing business needs.
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud vs Colocation
Growing businesses need IT solutions that can grow with them. Let’s explore how cloud and colocation handle increasing demands differently.
Cloud Scalability
Think of cloud resources like a water tap – you can adjust the flow instantly based on your needs. This IT scalability solution offers several advantages:
Instant Resource Adjustment
Need more processing power or storage? You can scale up in minutes. Running a seasonal business? Scale down during quiet periods to save money.
Geographic Expansion
Cloud services let you deploy resources in different locations quickly. This means you can serve customers from anywhere without building new infrastructure.
No Hardware Planning
You don’t need to predict your needs months in advance or worry about outgrowing your hardware. Resources are available when you need them.
Colocation Scalability
Colocation growth requires more planning but offers different advantages:
Physical Expansion Options
- Reserve additional rack space for future growth
- Upgrade existing hardware when needed
- Add new servers for specific projects
Resource Management
You control exactly how your resources grow and where they’re allocated. This can be particularly valuable for businesses with specific performance requirements.
Planning for Growth
The key difference lies in planning horizons:
- Cloud: Scale in minutes, pay for what you use
- Colocation: Plan months ahead, but maintain complete control
Consider your business’s growth pattern when choosing between cloud vs colocation. Fast-growing startups might prefer cloud flexibility, while businesses with steady, predictable growth might benefit from colocation’s planned expansion approach.
Next, let’s examine how each option handles security concerns.
Security Considerations: Which is More Secure?
Security keeps many small business owners awake at night, and rightly so. Let’s examine how cloud and colocation handle your data security needs differently.
Cloud Security
Cloud providers invest heavily in security, offering built-in protections that many small businesses couldn’t afford to implement themselves:
Data Protection
- Automatic encryption for stored data
- Regular security updates and patches
- Built-in firewall protection
- Automated backup systems
Compliance Support
Many providers offer tools and certifications to help meet data privacy regulations. This can be particularly valuable if you handle sensitive customer information.
Shared Responsibility
While providers secure the infrastructure, you’re still responsible for:
- Access management
- Application security
- Data classification
- User authentication
Colocation Security
Colocation facilities offer strong physical security while letting you control your digital security:
Physical Protection
- 24/7 facility monitoring
- Biometric access controls
- Environmental protections
- Video surveillance
Digital Security Control
You maintain complete control over your security measures, allowing for:
- Custom security configurations
- Specific compliance requirements
- Direct hardware access
- Tailored encryption solutions
Making the Security Choice
Your security needs depend on your business requirements. Cloud often works well for standard security needs, while colocation might be better if you need specific security configurations or have unique compliance requirements.
Next, let’s look at how these options compare in terms of performance and reliability.
Performance and Reliability: Cloud vs Colocation
Your IT infrastructure’s performance directly affects your daily operations. Let’s see how cloud vs colocation compare in keeping your business running smoothly.
Cloud Performance
Cloud environments offer consistent performance with built-in redundancy. Most providers offer service level agreements (SLAs) promising 99.9% or better uptime, meaning your services stay available even if some hardware fails.
Performance Features:
- Easy resource adjustment based on demand
- Automatic load balancing
- Built-in redundancy and backup
- Potential performance variations during peak times
Colocation Performance
With colocation, you control your hardware’s performance. Your servers run only your workloads, giving you consistent, predictable performance without sharing resources.
Key Benefits:
- Reliable power with backup systems
- Enterprise-grade cooling
- High-speed network connectivity
- Multiple internet providers for redundancy
Both options maintain high availability through different approaches – cloud through distributed systems and instant failover, colocation through physical redundancy and professional facility management.
Let’s explore how to choose the right solution for your specific business needs.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business
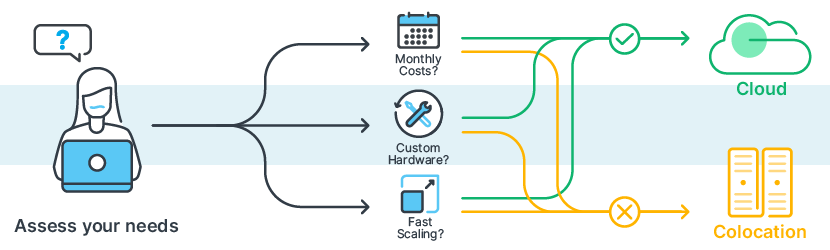
Making the right choice between cloud vs colocation starts with understanding your business needs. Let’s walk through a practical approach to this decision.
Budget and Costs
- Do you prefer predictable monthly payments or can you make upfront investments?
- How much can you invest in technical staff?
- What’s your expected growth rate over the next 1-2 years?
If you prefer monthly payments with minimal upfront investment, follow the budget path toward cloud solutions. If you can invest in hardware upfront, colocation might offer better long-term value.
Technical Requirements
- Do you need specific hardware configurations?
- How much control do you want over your infrastructure?
- What level of technical expertise does your team have?
- Can you manage hardware maintenance?
The technical path helps you assess whether you need custom hardware setups. Cloud works well for standard configurations, while colocation gives you complete hardware control.
Business Growth
- How quickly do you need to scale resources?
- Do you have seasonal fluctuations in demand?
- Where are your customers located?
- What are your security and compliance requirements?
The growth path looks at how quickly you need to scale. Fast-growing businesses often benefit from cloud flexibility, while steady growth patterns might work better with colocation.
Finding Your Fit
Cloud might be your best choice if you:
- Want to minimize upfront costs
- Need quick scalability
- Prefer managed services
- Have varying resource needs
Consider colocation if you:
- Need specific hardware setups
- Want complete control
- Have steady, predictable growth
- Already have technical expertise
Remember, these aren’t exclusive choices. Some businesses benefit from using both solutions for different needs.
Let’s look at some real-world examples to see how other small businesses made this decision.
Real-World Use Cases: Cloud and Colocation in Small Businesses
Let’s look at two examples of how businesses made cloud and colocation choices that delivered real results.
Healthcare Technology Success
Holt Systems, a healthcare software provider, made a strategic move to improve their service delivery. By transitioning to cloud services, they helped medical practices qualify for important healthcare programs, generating over $3M in revenue for their clients. Their choice of cloud hosting let them scale services quickly while maintaining healthcare compliance requirements.
Hybrid Approach
Waunakee Remodeling shows how traditional businesses can modernize effectively. They moved from basic backups to a hybrid approach, using cloud services for daily operations while keeping critical data in secure colocation facilities. This combination gave them both the flexibility of cloud and the security of dedicated hardware.
These examples show how your choice depends on your specific business needs. Let’s wrap up by helping you make the right choice for your business.
Conclusion: Which is Best for Your Small Business?
Choosing between cloud and colocation isn’t about finding the “best” solution – it’s about finding the right fit for your business. Let’s recap the key factors that should guide your decision.
When Cloud Makes Sense
Cloud hosting works best when you:
- Need flexibility to scale quickly
- Want predictable monthly expenses
- Prefer focusing on your business rather than IT management
- Don’t require specialized hardware
When Colocation Fits Better
Consider colocation when you:
- Need complete control over your hardware
- Have specific compliance requirements
- Want to leverage existing IT investments
- Have steady, predictable resource needs
Next Steps
Start by evaluating your current needs:
- List your specific requirements
- Review your budget structure
- Assess your technical capabilities
- Consider your growth plans
Remember, you can always start small and adjust your approach as your needs change. Whether you choose cloud, colocation, or a combination of both, focus on finding a solution that supports your business goals while matching your resources and capabilities.
