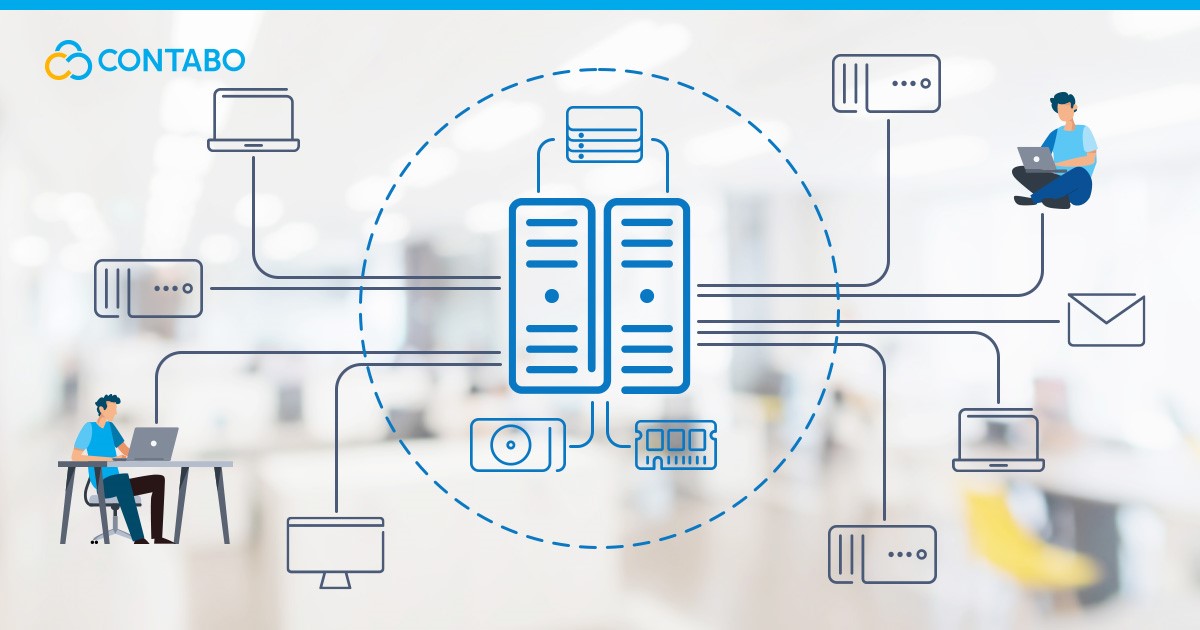
A terminal server is a powerful solution for businesses seeking to streamline their IT infrastructure and enable remote work. By centralizing applications and data running on a single server, they allow users to access these resources from any location, providing flexibility and efficiency in how work is done.
What is a Terminal Server?
A terminal server, fundamentally, is a server that allows multiple users to access and use applications and data stored on a server from remote locations. It acts as a central hub where all computing tasks occur, with the server managing these tasks and sending the information as well as the graphical interface back to the user’s device via a network. This setup enables the efficient use of resources, simplifies software management, and enhances security by centralizing data.
Terminal Servers vs. Desktop Virtualization vs. Remote Desktop – What’s the difference?
While terminal servers, desktop virtualization, and remote desktop services share the common goal of providing remote access, they differ significantly in their approach and implementation.
Terminal Servers focus on delivering applications and desktop environments, along with vital information, to multiple users from a central server. Each user interacts with the server through separate sessions, allowing for a shared but individualized computing experience. This setup ensures that users remain connected, facilitating seamless contact and collaboration across the network.
Desktop Virtualization involves creating a virtual version of a computer system, including the operating system, applications, and data. This technology allows for a more flexible and isolated environment for each user, as it can host multiple virtual desktops independently on a single physical server.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS), a feature of Windows Server, enables users to access graphical desktops and Windows applications from virtually any device. RDS is often used synonymously with terminal services, especially in the context of Windows servers, but it represents a broader category of remote access technologies, including both terminal services and desktop virtualization.
Terminal Servers vs. Cloud-Based Services
Terminal servers and cloud-based services offer distinct approaches to managing applications and data. While both provide solutions for remote work, their setup, applications, and operational models have key differences that suit varying business needs. Terminal servers are typically hosted on-premises and offer direct control over the IT environment, making them ideal for businesses with specific security and compliance requirements.
Cloud-based services, on the other hand, are hosted off-site by third-party providers, offering scalability and flexibility without the need for extensive hardware investment. Below is a comparison table that highlights the main differences between terminal servers and cloud-based services.
| Feature | Terminal Servers | Cloud-Based Services |
| Setup | On-premises infrastructure | Hosted by third-party providers |
| Control | High, with direct management of hardware and software | Limited, managed by service providers |
| Scalability | Dependent on physical hardware | Easily scalable with service plans |
| Cost | Upfront investment in hardware and software | Subscription-based, pay-as-you-go models |
| Security | Controlled internally, subject to in-house policies | Dependent on provider’s security measures |
| Accessibility | Through network connection to the server | Via internet from any device, anywhere |
How Terminal Servers Work and Their Applications
The Operational Framework of Terminal Servers
Terminal servers centralize applications and desktop environments on a server, enabling remote access over a network. This framework significantly reduces the need for high-end hardware for users, as the server manages all processing tasks. Users connect via a client application, which renders the desktop or application interface on their device, facilitating seamless remote work that feels as responsive as using a local machine.
Empowering Micro Businesses
For micro businesses, terminal servers are a game-changer, offering a cost-effective method to grant employees access to critical business applications without the hassle of individual software licenses and installations. Key applications include remote desktop access for flexible work locations, centralized file sharing for improved collaboration, and the ability of running specialized software without the need for high-powered local machines.
Ideal Beneficiaries
Organizations with the most to gain from terminal server technology include those operating on tight IT budgets, businesses that value high mobility and workforce flexibility, and companies aiming to simplify their IT management. Educational institutions can provide access to learning applications without a full computer lab; small healthcare providers manage patient records more efficiently; and startups maintain agile development environments—all without the steep costs of traditional IT infrastructure. Terminal servers offer a scalable and versatile solution, especially for entities aiming to maximize resource efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Setting Up a Terminal Server: Infrastructure Essentials
Deploying a terminal server demands a careful selection of hardware and software. Essential hardware includes a high-performance CPU, enough RAM, and sufficient storage to support multiple users simultaneously. Software choices typically revolve around the operating system, with Windows Server and Linux/Ubuntu being popular options.
Choosing Between Windows and Linux/Ubuntu
Windows Server offers seamless integration with Microsoft products, providing a familiar environment for users and administrators. Linux/Ubuntu appeals for its flexibility and cost-effectiveness, suitable for those with the expertise to customize their setup. Both support a wide range of applications and can be tailored to specific needs.
Citrix and VMWare: Enhancing Terminal Services
Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops deliver a high-definition user experience on any device, while VMWare Horizon offers scalable virtual desktop and application virtualization with robust security features. These platforms extend the capabilities of the basic operating system, providing enhanced functionality and management options.
Security, Privacy, and Licensing Compliance
Security and privacy are critical, necessitating strong access controls, encryption, and adherence to licensing agreements. Both Microsoft and Linux have specific licensing requirements for terminal services, as do Citrix and VMWare. Ensuring compliance with these licenses and maintaining high data protection standards is essential for a secure and legal operation.
Addressing these essentials enables organizations to set up a terminal server environment that is efficient, secure, and aligned with their operational requirements.
Costs, Advantages, and Challenges
Implementing terminal server technology involves initial setup costs, including hardware acquisition, software licensing, and potential infrastructure upgrades. Maintenance costs vary, depending on the scale of the deployment and ongoing support needs. While upfront expenses can be significant, the long-term savings on individual workstation upgrades and software licenses often justify the investment.
Advantages
Terminal servers centralize application management, reducing IT workload and hardware costs by eliminating the need for high-end user devices. They enable remote access, enhancing flexibility and productivity for users. Additionally, centralized data storage improves security and simplifies backup procedures.
Challenges
However, terminal servers can face scalability limits, requiring careful planning to accommodate user growth. Performance issues may arise if the server’s resources are stretched too thin, affecting user experience. Ensuring data security and compliance also becomes more complex with centralized storage.
Best Practices
To mitigate these challenges, adopt scalable hardware solutions and regularly review server performance. Implement robust security measures, including encryption and access controls, and stay compliant with licensing requirements. Regularly updating software and hardware components ensures efficiency and security. Following these best practices helps maintain a stable and effective terminal server architecture, maximizing the benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Compatibility, Access, and Alternatives
Terminal servers boast remarkable device compatibility, supporting a wide range of client devices from traditional desktops to modern smartphones. This flexibility ensures users can access their applications and data from virtually anywhere, provided they have an internet connection. The use of standard protocols like Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) facilitates this broad compatibility, making terminal servers a versatile choice for businesses seeking to accommodate diverse user preferences and working styles.
Alternatives to Terminal Servers
While terminal servers offer a robust solution for remote access and management, organizations might consider alternatives like cloud computing services and Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI). Cloud services provide scalable resources on demand, eliminating the need for on-premises hardware. VDI, on the other hand, offers a more personalized desktop experience, with each user getting a dedicated virtual machine. These alternatives can offer different benefits in terms of scalability, cost, and management requirements, allowing organizations to choose the best fit for their
Implementing Terminal Servers with Contabo
Starting with terminal servers at Contabo is straightforward. The initial step involves selecting the right server product that aligns with your business needs. Contabo offers a variety of server options, each with different performance levels and customization possibilities to ensure you find the perfect match for your requirements. We recommend one server out of our Dedicated Servers lineup. The setup process is designed for simplicity, allowing for quick deployment.
VDI-Pre-Configured Products
Contabo also provides VDI-pre-configured products, which come with the advantage of being ready to use out of the box. These solutions are ideal for businesses looking for a hassle-free start, eliminating the need for extensive setup and configuration. The benefits include optimized performance for virtual desktop environments, scalability to grow with your business, and enhanced security features. Choosing a VDI-pre-configured product from Contabo can significantly streamline the implementation process, making it easier to leverage the power of terminal servers.
FAQs and Troubleshooting
When navigating the world of terminal servers, users may encounter common hurdles that can impact their experience. Addressing these effectively ensures smooth operation and user satisfaction.
- Access Denial: Often related to incorrect login credentials or insufficient user permissions. Verify user details and ensure they have the right access level.
- Black Screen on Login: This issue can stem from connectivity problems or server-side graphics settings. Checking the network connection and server configuration can help resolve this.
- Session Timeouts: Usually due to network instability or server settings. Ensuring a stable internet connection and adjusting the server’s timeout settings can mitigate the problem of sessions timing out.
- Maximum Connection Limits: When the server reaches its user capacity, new logins are denied. Upgrading server resources or optimizing current usage can provide a solution.
Conclusion
Terminal servers represent a pivotal technology for micro-businesses, offering a cost-effective, flexible solution for remote access and centralized application management. By consolidating resources and simplifying IT infrastructure, these servers enable businesses to enhance productivity and security while reducing overhead costs. The adaptability of terminal servers, coupled with their compatibility across various devices, ensures that businesses can scale and adapt to future demands without significant reinvestment. Embracing terminal server technology not only meets the immediate needs of a dynamic workforce but also positions micro businesses for sustainable growth and resilience in the evolving digital landscape.
