With this tutorial we will explain certain types of RAID levels to you.
Some of you might have already experienced a loss of data, no matter if it was an SD card holding some vacation photos or a hard disk holding important files. Losing data can be very costly if you try to restore them by some specialist. An expert is needed and the procedure takes a lot of time, the easiest way to avoid those costs is simply to avoid any data loss in the first place.
This overview is not relevant for any VPS, your VPS systems are already running safe on a RAID system monitored by experienced technicians.
Creating backups is still very important, a RAID does not replace any backup!
You can find further instructions within the following tutorial: Data loss and how to avoid it
There are some points which you should think about first, there are several results depending on your requirements.
- How important is the performance?
- How much data security should be provided by the RAID?
- Are system resources available to manage the RAID, such as CPU and RAM
Depending on the results of the above questions and your budget, there are several options available:
A hardware RAID is always more expensive but provides the best performance and security (if combined with a battery backup unit).
A software RAID is the easiest way to go for a RAID, it is able to handle almost any type of RAID and can be set up within a few minutes.
An overview of available RAID levels is shown below:
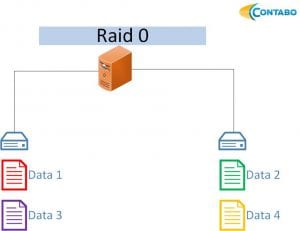
RAID 0
The RAID 0 provides increased write and read performance, the data will be distributed to at least two disks. Since there is no redundancy all data will be lost in case one disk fails.
- At least two hard disks are needed
- No disk redundancy at all
- Maximum (complete) storage capacity available
- Improved read and write performance
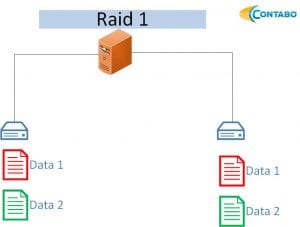
RAID 1
The RAID 1 provides increased read performance (depending on the software/hardware controller used), all data will be mirrored to a second disk. There is also a RAID 1E available – in that case all data will be mirrored to additional disks too.
- At least two hard disks are needed
- n-1 disks can fail
- 1/n of storage available (n = number of disks, with two disks = > 1/2 of total storage)
- Improved read performance
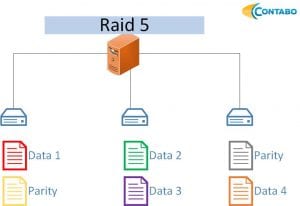
RAID 5
The RAID 5 provides increased write and read performance, the data is written to at least two disks, an additional disk is always used for storing parity data. The parity data has to be calculated for every write – so for very write intensive applications the RAID 5 requires a lot of performance due to the necessary calculations.
- At least three hard disks are needed
- One disk can fail
- n-1/n of storage available (n = number of disks, with three disks = > 2/3 of total storage)
- Improved read and write performance
- Requires a lot of CPU time
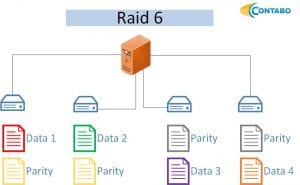
RAID 6
The RAID 6 provides increased read performance, the data is written to at least two disks, two additional disks are always used for storing parity data. The parity data has to be calculated for every write – so for very write intensive applications the RAID 6 requires a lot of performance due to the necessary calculations. As there are two parity bits saved on the disks, the needed CPU time is very high.
- At least four hard disks are needed
- Two disks can fail simultaneously
- n-2/n of storage available (n = number of disks, with two disks = > 2/4 (half) of total storage)
- Improved read performance
- Requires the most CPU time
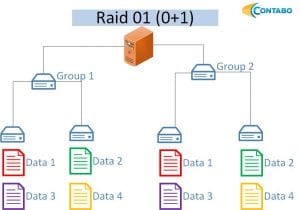
RAID 01
A RAID 01 is a combination of two or more volume groups. Each volume group is configured to have a RAID 0, those volume groups are mirrored in a RAID 1. With a total number of four disks one entire volume group can fail with both disks and no data will be lost.
- At least four hard disks are needed
- Two disks can fail simultaneously if they belong to the same logical volume group
- Half of total storage capacity is available
- Improved read and write performance
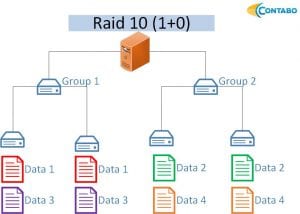
RAID 10
A RAID 10 is a combination of two or more volume groups. Each volume group is configured to have a RAID 1, those volume groups are striped in a RAID 0. With a total number of four disks, two disks can fail simultaneously and no data will be lost – the failed disks must not belong to the same volume group.
- At least four hard disks are needed
- Two disks can fail simultaneously if they do not belong to the same logical volume group
- Half of total storage capacity is available
- Improved read and write performance
The difference between RAID 01 and RAID 10 is only visible with six or more disks, if you have six disks a RAID 10 will provide a higher calculated security rate. We do recommend using a RAID 10 instead of using a RAID 01 even if you do only have four disks. Some RAID controllers do not even support a RAID 01 anymore. RAID 5 and RAID 6 require the highest CPU time since a checksum has to be calculated on every writing process to the disk. Only a few enterprise RAID controllers do support RAID 5 and RAID 6, due to the need of calculating checksums the writing speed might suffer which might then cause problems when using write intensive applications.
For our dedicated servers it is always possible to order additional hard disks or RAID controllers, current prices can be found on our web site. If you need a special configuration, please contact our support team any day between 8 am and 11 pm (German timezone, UTC+2).
Zu Anti-Banner hinzufügen
